Rho kinase inhibitor
Rho kinase inhibitors (rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor or ROCK inhibitor) are a series of compounds that target rho kinase (ROCK). Clinical trials have found that inhibition of the ROCK pathway contributes to the cardiovascular benefits of statin therapy. Furthermore, ROCK inhibitors may have clinical applications for anti-erectile dysfunction, antihypertension, and tumor metastasis inhibition.[1] More recently they have been studied for the treatment of glaucoma[2] and as a therapeutic target for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, including ischemic stroke.[3] While statin therapy has been demonstrated to reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events, including ischemic stroke,[4] the interplay between the ROCK pathway and statin therapy to treat and prevent strokes in older adults has not yet been proven.[3]
Examples
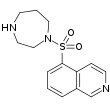
- Fasudil, its hydrochloride salt is a drug currently not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In Japan and China it is used for improvement and prevention of cerebral vasospasm and the cerebral ischemic symptoms caused by it after subarachnoid hemorrhage surgery.
- Ripasudil, used in Japan for the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
- Netarsudil, approved in United States for glaucoma and ocular hypertension.[5]
- RKI-1447, a potent small molecule inhibitor of ROCK1 and ROCK2.[6] Studies show that RKI-1447 could have anti-invasive and anti-tumor activities.
- Y-27632, the first small molecule ROCK inhibitor. It selectively inhibits ROCK1 with Ki of 140 nM.[7]
- GSK429286A, C21H16F4N4O2[8]
- Y-30141
References
- Liao JK, Seto M, Noma K (July 2007). "Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitors". J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 50 (1): 17–24. doi:10.1097/FJC.0b013e318070d1bd. PMC 2692906. PMID 17666911.
- Wang SK, Chang RT (2014). "An emerging treatment option for glaucoma: Rho kinase inhibitors". Clin Ophthalmol. 8: 883–90. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S41000. PMC 4025933. PMID 24872673.
- Sladojevic, Nikola; Yu, Brian; Liao, James K. (2017-12-02). "ROCK as a therapeutic target for ischemic stroke". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 17 (12): 1167–1177. doi:10.1080/14737175.2017.1395700. ISSN 1473-7175. PMC 6221831. PMID 29057688.
- O’Brien, Emily C.; Greiner, Melissa A.; Xian, Ying; Fonarow, Gregg C.; Olson, DaiWai M.; Schwamm, Lee H.; Bhatt, Deepak L.; Smith, Eric E.; Maisch, Lesley (2015-10-13). "Clinical Effectiveness of Statin Therapy After Ischemic Stroke: Primary Results From the Statin Therapeutic Area of the Patient-Centered Research Into Outcomes Stroke Patients Prefer and Effectiveness Research (PROSPER) Study". Circulation. 132 (15): 1404–1413. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.016183. ISSN 0009-7322. PMID 26246175.
- (PDF) https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/208254lbl.pdf. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - Patel RA, Forinash KD, Pireddu R, Sun Y, Sun N, Martin MP, Schönbrunn E, Lawrence NJ, Sebti SM (October 2012). "RKI-1447 is a potent inhibitor of the Rho-associated ROCK kinases with anti-invasive and antitumor activities in breast cancer". Cancer Res. 72 (19): 5025–34. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0954. PMC 3463757. PMID 22846914.
- "information of different kinds of ROCK inhibitor". selleckchemicals.
- GSK429286A@pubchem