Rhône Glacier
The Rhône Glacier (German: Rhonegletscher, Walliser German: Rottengletscher, French: glacier du Rhône, Italian: ghiacciaio del Rodano) is a glacier in the Swiss Alps and the source of the river Rhône and one of the primary contributors to Lake Geneva in the far eastern end of the Swiss canton of Valais. Because the glacier is located close to the Furka Pass road it is easily accessible.
| Rhône Glacier | |
|---|---|
| German: Rhonegletscher, French: Glacier du Rhône, Italian: ghiacciaio del Rodano | |
 View towards the Tieralplistock | |
| Type | Valley glacier |
| Location | Furkapass, Valais, Switzerland |
| Coordinates | 46°34.32′N 8°22.58′E |
| Area | 17.60 km2 (6.80 sq mi) (1973) |
| Length | 9.09 km (5.65 mi) (1879), 8.00 km (4.97 mi) (1973), 7.65 km (4.75 mi) (2016) |
| Highest elevation | 3,630 m (11,910 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 2,200 m (7,200 ft) |
| Terminus | Rotten (local name for Rhône) above Gletsch |
| Status | Retreating |
Geography
The Rhône Glacier is the largest glacier in the Urner Alps. It lies on the south side of the range at the source of the Rhône. The Undri Triftlimi (3,081 m) connects it to the Trift Glacier. The glacier is located on the northernmost part of the canton of Valais, between the Grimsel Pass and the Furka Pass and is part of the Oberwald municipality. The Dammastock (3,630 m) is the highest summit above the glacier.
Evolution
 2018
2018 2010
2010 2008
2008- 2005
 1900
1900 1870
1870
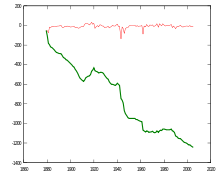
Vertical axis: length difference in meters
Horizontal axis: years
In thick green: cumulated length difference starting 1879
In thin red: growth during one year
The Rhône Glacier is easily accessible so its evolution is observed since the 19th century. The glacier lost ~1300 m during the last 120 years leaving behind a track of naked stone.
Slowing the retreat
For several years, UV-resistant fleecy white blankets have been installed during the warm periods, covering about 5 acres of the retreating glacier to reduce its melting.[1] It's estimated that this effort reduces the melting by up to 70%.[2][3] In addition to the global implications of increasing climate warming and instability, the local economy is at risk of losing business income from glacier tourists who have flocked to the area since 1870 to walk through "a long and winding ice grotto with glistening blue walls and a leaky ceiling".[4]
References
- Mallonee, Laura. "Switzerland Tries to Save a Glacier... by Covering It in Blankets". WIRED. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
- Harvey, Chelsea. "GEOENGINEERING: Can we refreeze the Arctic? Scientists are beginning to ask". www.eenews.net. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
- Carylsue (2018-03-14). "Switzerland Protects the Alps with a Blanket". National Geographic Education Blog. Retrieved 2019-10-26.
- Larson, Nina. "Blankets cover Swiss glacier in vain effort to halt icemelt". Yahoo. Agence France-Presse/AFP. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
- Rhône Glacier at Glaciers online
- Rhône Glacier at NASA Earth Observatory
External links
- Simulation of the shrinking of the glacier
- Swiss Glacier Monitoring Network: Rhône Glacier - with length variation measurements since 1879

- Interactive repeat photo comparisons of the Rhône Glacier