Retronecine
Retronecine is a pyrrolizidine alkaloid found in a variety of plants in the genera Senecio and Crotalaria, and the family Boraginaceae. It is the most common central core for other pyrrolizidine alkaloids.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
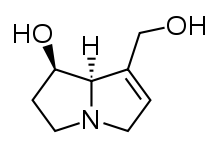
| IUPAC name
(1R,7aR)-7-(Hydroxymethyl)-2,3,5,7a-tetrahydro-1H-pyrrolizin-1-ol | |
| Other names
(+)-Retronecine; Retronecin; Senecifolinene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H13NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 155.197 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 119 to 120 °C (246 to 248 °F; 392 to 393 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
634 mg/kg (IV, mouse)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.