Regrowth inside ballast tanks
After delivering their cargo, empty commercial ships need to take up water from the port of arrival in order to maintain stability and ensure safe navigation conditions before heading back to the port of departure. This water, called ballast water, which contains aquatic organisms typical of the port of arrival, is stored in ballast tanks and is ultimately discharged at the port of departure when the ship is ready to be re-loaded. During this process, aquatic organisms capable of surviving in ballast water are released into new environments and can therefore become invasive species, causing serious economic and public health issues.[1][2]
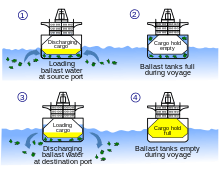
Following the ratification of the International Maritime Organization (IMO)’s Ballast Water Management (BWM) Convention, commercial ships will have to treat their ballast water in order to comply with maximum discharge standards established for organisms in different size categories (IMO’s D-2 Standards and US Coast Guard Standards). However, some organisms are capable of surviving or even recovering after harsh treatments, leading to regrowth in ballast water tanks before discharge. In order to minimise regrowth and hence avoid exceeding discharge limits, different criteria such as duration of the journey, ballast water tanks capacity and water flow rate at intake and discharge, among others, should be considered when choosing an appropriate type-approved ballast water treatment systems (BWTS).
Ballast water treatment systems (BWTS)
As of 2012, no single ballast water treatment method, or even a combination of primary (e.g. mechanical/physical separation) and secondary (e.g. active chemical substances) methods, can remove or inactivate all organisms in ballast water.[3][4][5][6][7][8] Furthermore, some treatments are more effective in removing microorganisms such as bacteria, whereas others are better at killing larger organisms such as phytoplankton (e.g. diatoms) and zooplankton (e.g. copepods).[3][6][9][10]
There are currently over 50 IMO type-approved BWTS on the market to choose from. These include the use of technologies such as UV irradiation, ozonation, electrochlorination, hydrodynamic cavitation and ultrasound, among others, applied as stand-alone or combined treatments.[6][10] The US Coast Guard requires BWTS as per 46 CFR 162.060,[11][12] and began approving in 2016.[13]
Regrowth
Surviving organisms have the potential to regrow after treatment and, depending on the duration of the voyage and the prevailing conditions, this regrowth could lead to exceeding the maximum number of aquatic organisms that can be discharged according to the established standards.
Both phytoplankton and zooplankton have been shown to be capable of surviving in ballast water tanks for up to 23 days.[14][15] There is also evidence showing that different phytoplanktonic organisms can regrow within 4 to 20 days of incubating in favourable conditions.[16][17][18][19][20] Bacteria that survive treatment have an even higher potential for regrowth, as they benefit from the death of other organisms in two different ways (i) nutrients essential for bacterial growth are released in the form of dissolved organic matter and, (ii) there is a decrease in the number of predators that would otherwise eat them.[21][22][23][24] Overall, bacterial regrowth has been observed after 18 hrs to 7 days of applying different treatments.[4][24][25][26][27]
Therefore, the scientific evidence currently available supports the idea that it is not an issue of “IF regrowth” but “WHEN regrowth”.
Considerations
Timescales are very important when considering regrowth. For instance, if ballast water is treated at intake and held in ballast tanks for over a week before discharge, then the organisms surviving the treatment could have enough time to increase in numbers and potentially exceed discharge standards before the end of the voyage.
Every BWTS has its advantages and disadvantages [10] and ship owners and ship operators should consider the benefits and limitations of different systems before making an educated choice based on their requirements. The issue of regrowth should be taken seriously and should be taken into account when choosing an appropriate BWTS.[28]
See also
- Ballast Water Management
- Environmental impact of shipping
References
- "Silent Invasion" (PDF). WWF International. 2009.
- "Control and management of ballast water". gov.uk. 2012.
- Chase, C., Reilly, C., Pederson, J. (2001) Marine bioinvasions fact sheet: ballast water treatment options. MIT Sea Grant Centre for Coastal Resources, Cambridge, MA. Marine bioinvasions fact sheet.
- Waite, T.D., Kazumi, J., Lane, P.V.Z., Farmer, L.L., Smith, S.G., Smith, S.L., Hitchcock, G., Capo, T.R. (2003). Waite, T.D., Kazumi, J., Lane, P.V.Z., Farmer, L.L., Smith, S.G., Smith, S.L., Hitchcock, G., Capo, T.R. (2003). “Removal of natural populations of marine plankton by a large-scale ballast water treatment system”. Marine Ecology Progress Series 258: 51-63.
- Tsolaki, E., Diamadopoulos, E. (2010). “Technologies for ballast water treatment: a review”. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology 85: 19-32.
- Gregg, M., Rigby, G., Hallegraeff, G.M. (2009). “Review of two decades of progress in the development of management options for reducing or eradicating phytoplankton, zooplankton and bacteria in ship’s ballast water”. Aquatic Invasions 4, 521-565.
- Veldhuis, M., ten Hallers, C., de la Rivière, E.B., Fuhr, F., Finke, J., Stehouwer, P.P., van de Star, I., van Slooten, C. (2010). “Ballast water treatment systems: “Old” and “New” ones”. In: Emerging ballast water management systems. Proceedings of the IMO-WMU Research and Development Forum, Malmö, Sweden.
- Ibrahim, A.M., El-Naggar, M.M. (2012). “Ballast water review: impacts, treatments and management”. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 12: 976-84.
- Wright, D., Dawson, R. (2002). “Shipboard Trial of Primary and Secondary Ballast Water Treatment Systems”. In: Ballast Water Treatment R&D Directory.
- Ballast water treatment technologies and current system availability (2015). Part of Lloyd's Register's Understanding Ballast Water Management Series.
- "Title 46 → Chapter I → Subchapter Q → Part 162 → Subpart 162.060". United States Coast Guard. December 6, 2016. Retrieved December 8, 2016.
- "Homeport: Ballast Water Management Program". United States Coast Guard. Retrieved December 8, 2016.
- "Marine Safety Center issues Ballast Water Management System (BWMS) type-approval certificate to Optimarin AS". United States Coast Guard. December 2, 2016. Retrieved December 8, 2016.
- Kang, J.H., Hyun, B.G., Shin, K. (2010). “Phytoplankton viability in ballast water from international commercial ships berthed at ports in Korea”. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60: 230-237.
- Gollasch, S., Lenz, J., Dammer, M., Andres, H.G. (2000). “Survival of tropical ballast water organisms during a cruise from the Indian Ocean to the North Sea”. Journal of Plankton Research 22: 923-937.
- Stehouwer, P.P., Fuhr, F., Veldhuis, M. (2010). “A novel approach to determine ballast water vitality and viability after treatment”. In: Emerging ballast water management systems. Proceedings of the IMO-WMU Research and Development Forum, Malmö, Sweden.
- Stehouwer, P.P., Buma, A., Peperzak, L. (2015). “A comparison of six different ballast water treatment systems based on UV radiation, electrochlorination and chlorine dioxide”. Environmental Technology 36: 2094-2104.
- van der Star, I., Liebich, V., Stehouwer, P.P. (2011). “The forgotten fraction: The importance of organisms smaller than 10 µm when evaluating ballast water treatment systems”. Ballast Water Management Systems 41.
- Liebich, V., Stehouwer, P.P., Veldhuis, M. (2012). “Regrowth of potential invasive phytoplankton following UV-based ballast water treatment”. Aquatic Invasions 7: 29-36.
- Martínez, L.F., Mahamud, M.M., Lavín, A.G., Bueno, J.L. (2013). “The regrowth of phytoplankton cultures after UV disinfection”. Marine Pollution Bulletin 67: 152-157.
- Carney, K.J., Delany, J.E., Sawant, S., Mesbahi, E. (2011). “The effects of prolonged darkness on temperate and tropical marine phytoplankton, and their implications for ballast water risk management”. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62: 1233-1244.
- Lasternas, S., Agustí, S. (2014). “The percentage of living bacterial cells related to organic carbon release from senescent oceanic phytoplankton”. Biogeosciences 11: 6377-6387.
- Buchan, A., LeCleir, G.R., Gulvik, C.A., González, J.M. (2014). “Master recyclers: features and functions of bacteria associated with phytoplankton blooms”. Nature Reviews Microbiology 12: 686-698.
- Hess-Erga, O.K., Blomvågnes-Bakke, B., Vadstein, O. (2010). “Recolonization by heterotrophic bacteria after UV irradiation or ozonation of seawater; a simulation of ballast water treatment”. Water Research 44: 5439-5449.
- Li, D., Zeng, S., Gu, A.Z., He, M., Shi, H. (2013). “Inactivation, reactivation and regrowth of indigenous bacteria in reclaimed water after chlorine disinfection of a municipal wastewater treatment plant”. Journal of Environmental Sciences 25: 1319-1325.
- van Slooten, C., Peperzak, L., Buma, A.G. (2015). “Assessment of didecyldimethylammonium chloride as a ballast water treatment method”. Environmental Technology 36: 435-449.
- First, M.R., Drake, L.A. (2014). “Life after treatment: detecting living microorganisms following exposure to UV light and chlorine dioxide”. Journal of Applied Phycology 26: 227-235.
- Grob, C., Pollet, B.G. (2016). “Regrowth in ship’s ballast water tanks: think again!”. Accepted for publication in Marine Pollution Bulletin.