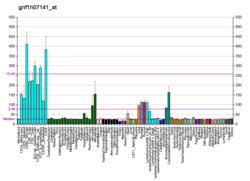
ROBO2
Roundabout homolog 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ROBO2 gene.[5][6]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000185008 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000052516 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Kidd T, Brose K, Mitchell KJ, Fetter RD, Tessier-Lavigne M, Goodman CS, Tear G (Feb 1998). "Roundabout controls axon crossing of the CNS midline and defines a novel subfamily of evolutionarily conserved guidance receptors". Cell. 92 (2): 205–15. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80915-0. PMID 9458045.
- "Entrez Gene: ROBO2 roundabout, axon guidance receptor, homolog 2 (Drosophila)".
Further reading
- Brose K, Bland KS, Wang KH, et al. (1999). "Slit proteins bind Robo receptors and have an evolutionarily conserved role in repulsive axon guidance". Cell. 96 (6): 795–806. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80590-5. PMID 10102268.
- Nguyen Ba-Charvet KT, Brose K, Marillat V, et al. (1999). "Slit2-Mediated chemorepulsion and collapse of developing forebrain axons". Neuron. 22 (3): 463–73. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80702-3. PMID 10197527.
- Nagase T, Kikuno R, Nakayama M, et al. (2001). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XVIII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 7 (4): 273–81. doi:10.1093/dnares/7.4.271. PMID 10997877.
- Nguyen Ba-Charvet KT, Brose K, Ma L, et al. (2001). "Diversity and specificity of actions of Slit2 proteolytic fragments in axon guidance". J. Neurosci. 21 (12): 4281–9. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-12-04281.2001. PMID 11404413.
- Marillat V, Cases O, Nguyen-Ba-Charvet KT, et al. (2002). "Spatiotemporal expression patterns of slit and robo genes in the rat brain". J. Comp. Neurol. 442 (2): 130–55. doi:10.1002/cne.10068. PMID 11754167.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Hivert B, Liu Z, Chuang CY, et al. (2003). "Robo1 and Robo2 are homophilic binding molecules that promote axonal growth". Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 21 (4): 534–45. doi:10.1006/mcne.2002.1193. PMID 12504588.
- Grieshammer U, Le M, Plump AS, et al. (2004). "SLIT2-mediated ROBO2 signaling restricts kidney induction to a single site". Dev. Cell. 6 (5): 709–17. doi:10.1016/S1534-5807(04)00108-X. PMID 15130495.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Yue Y, Grossmann B, Galetzka D, et al. (2007). "Isolation and differential expression of two isoforms of the ROBO2/Robo2 axon guidance receptor gene in humans and mice". Genomics. 88 (6): 772–8. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.05.011. PMID 16829019.
- Lu W, van Eerde AM, Fan X, et al. (2007). "Disruption of ROBO2 is associated with urinary tract anomalies and confers risk of vesicoureteral reflux". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80 (4): 616–32. doi:10.1086/512735. PMC 1852714. PMID 17357069.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.