RNAI
RNAI is a non-coding RNA that is an antisense repressor of the replication of some E. coli plasmids, including ColE1. Plasmid replication is usually initiated by RNAII,[1] which acts as a primer by binding to its template DNA. The complementary RNAI binds RNAII prohibiting it from its initiation role. The rate of degradation of RNAI is therefore a major factor in the control of plasmid replication. This rate of degradation is aided by the pcnB (plasmid copy number B) gene product,[2] which polyadenylates the 3' end of RNAI targeting it for degradation by PNPase.[3]
| RNAI | |
|---|---|
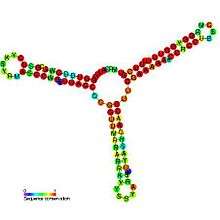 Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of RNAI | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | RNAI |
| Rfam | RF00106 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; antisense |
| Domain(s) | Bacteria |
| SO | 0000644 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
References
- Masukata H, Tomizawa J (January 1986). "Control of primer formation for ColE1 plasmid replication: conformational change of the primer transcript". Cell. 44 (1): 125–136. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(86)90491-5. PMID 2416472.
- He L, Söderbom F, Wagner EG, Binnie U, Binns N, Masters M (September 1993). "PcnB is required for the rapid degradation of RNAI, the antisense RNA that controls the copy number of ColE1-related plasmids". Molecular Microbiology. 9 (6): 1131–1142. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01243.x. PMID 7523833.
- Xu F, Lin-Chao S, Cohen SN (July 1993). "The Escherichia coli pcnB gene promotes adenylylation of antisense RNAI of ColE1-type plasmids in vivo and degradation of RNAI decay intermediates". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 90 (14): 6756–6760. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.14.6756. PMC 47011. PMID 7688127.
Further reading
- Cohen SN (March 1995). "Surprises at the 3' end of prokaryotic RNA". Cell. 80 (6): 829–832. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90284-8. PMID 7535193.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.