Purple honeycreeper
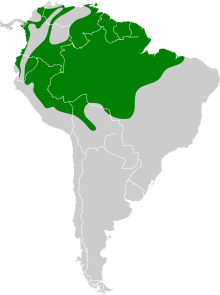
The purple honeycreeper (Cyanerpes caeruleus) is a small bird in the tanager family. It is found in the tropical New World from Colombia and Venezuela south to Brazil, and on Trinidad. A few, possibly introduced birds have been recorded on Tobago. The species is a bird of northern South America, and besides the Amazon Basin and the Guianas, a coastal range occurs west of the Andes, including parts of southern Panama. In the south, its range extends to the extreme western Pantanal. Though it is most frequently seen in the lowlands up to 3,300 ft (1,000 m) ASL or so, it has been encountered as high as 7,500 ft (2,300 m) ASL.[2]
| Purple honeycreeper | |
|---|---|
_male.jpg) | |
| Adult male C. c. longirostris, Trinidad | |
_female.jpg) | |
| Adult female C. c. longirostris, Trinidad | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Thraupidae |
| Genus: | Cyanerpes |
| Species: | C. caeruleus |
| Binomial name | |
| Cyanerpes caeruleus | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Certhia caerulea Linnaeus, 1758 | |
The purple honeycreeper is 4.5 in (11.5 cm) long, weighs 0.42 oz (12 g) and has a long black decurved bill. The male is purple with black wings, tail and belly, and bright yellow legs. Females and immatures have green upperparts, and green-streaked yellowish-buff underparts. The throat is cinnamon, and there is a blue moustachial stripe. The call of purple honeycreeper is a thin high-pitched zree.
The Trinidadian subspecies C. c. longirostris has a longer bill than the mainland forms.
This is a forest canopy species, but also occurs in cocoa and citrus plantations. At the upper limit of its altitudinal range, it frequents premontane rainforest, usually rather low-growing (33–50 ft/10–15 m) and full of epiphytes and mosses, and even elfin forest and páramo.[2]
The purple honeycreeper is often found in small groups. It feeds on nectar (particularly from bromeliad and similar flowers, to which its bill shape is adapted), berries and insects, mainly in the canopy. It is a bold and inquisitive bird, responding readily to the call of the ferruginous pygmy owl (Glaucidium brasilianum) by coming out of cover and searching for the presumed predator to mob it. The female purple honeycreeper builds a small cup nest in a tree, and incubates the clutch of two brown-blotched white eggs.
_juvenile_male_2.jpg) Juvenile male C. c. longirostris, Trinidad
Juvenile male C. c. longirostris, Trinidad_03.jpg) Adult male at Vienna Zoo, Austria, legs are pale in captive birds
Adult male at Vienna Zoo, Austria, legs are pale in captive birds Female at Diergaarde Blijdorp, Netherlands
Female at Diergaarde Blijdorp, Netherlands
Footnotes
- BirdLife International (2012). "Cyanerpes caeruleus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Salaman et al. (2002)
References
- ffrench, Richard; O'Neill, John Patton & Eckelberry, Don R. (1991): A guide to the birds of Trinidad and Tobago (2nd edition). Comstock Publishing, Ithaca, N.Y.. ISBN 0-8014-9792-2
- Hilty, Steven L. (2003): Birds of Venezuela. Christopher Helm, London. ISBN 0-7136-6418-5
- Salaman, Paul G.W.; Stiles, F. Gary; Bohórquez, Clara Isabel; Álvarez-R., Mauricio; Umaña, Ana María; Donegan, Thomas M. & Cuervo, Andrés M. (2002): New and noteworthy bird records from the east slope of the Andes of Colombia. Caldasia 24(1): 157–189. PDF fulltext
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cyanerpes caeruleus. |
- Purple Honeycreeper videos on the Internet Bird Collection
- Purple Honeycreeper photo gallery VIREO
- Photo-High Res; Article www.tsgcs.co.uk
- Photo-High Res—Green female-(Close-up); Article stevenrotsch Photo--(male)
