Puntal dels Llops
Puntal dels Llops is a small Iberian hilltop fort located near the modern town of Olocau, in Valencia province. It overlies an earlier Bronze Age site.[1] Its original name in Iberian is unknown. It was built in the late fifth or early fourth century BC and destroyed violently around the end of the Second Punic War or in the early second century BC. The site is part of a network of fortified sites that surround the large Iberian town of Edeta (Tossal de Sant Miguel, Llíria) and so is important to understanding the formation and organisation of Iberian polities.[2] The archaeological site may currently be visited.

Site layout and artifacts
Puntal dels Llops is a small (0.06 hectare) enclosed settlement where the perimeter wall is also the back wall of the rooms, which then face onto a central street.[3] This style (a "village clos" or "poblado de calle central") was introduced in the northeast of the Iberian Peninsula in the Bronze Age but continued to be used for some Iron Age Iberian settlements.[4] The entrance is on the most easily accessible side and so is the most defended point, with a tower, a dog-leg entrance, ditches and an additional low outer rampart.[5] The site had seventeen rooms, at least some of which were originally two stories high, with steps to the upper floor located on the street.[6]
Due to the violent destruction and consequent abrupt abandonment of the site, many objects were found in the different rooms, providing clues to their original function. Because the different rooms do not each have a full set of implements for cooking, dining and carrying out other daily tasks and especially because of the lack of hearths in many of the rooms, the community should not be seen as inhabited by several separate households.[7] In addition, a couple of the rooms (1 & 2) concentrate ritual items with prestigious imported ceramics while another room (4) contains the equipment for a single warrior on horseback: with horse trappings, a sword, knives and one of the two spear-heads found at the site.[8][9] As such, investigators have suggested that the community consisted of one aristocratic man or family accompanied by relatives, clients and servants.[10] The total number of inhabitants was probably between twenty and sixty.[11]
Room 1 stands out for its sacred character.[9] An infant burial was located under the floor. The room also contained a large hearth with impressive paving and the highest proportion of imported Black Gloss ceramics (from Campania and Attica). Amongst the imported and local ceramics were small vases and jars for pouring libations, incense burners in the shape of the head of a goddess, lamps and many cups. The room also had a large esparto mat, an iron key, and a set of weights with a balance. The room contained more common items as well, such as loom weights, spindle whorls and large storage containers. On the other hand, no cooking ware was found in the room. In the next room (2) was an area for separating silver from lead, along with evidence for textile manufacture and cooking. In recent work, the authors have proposed that there is a gendering of the space, with ritual activities, cupellation, weaving, cooking and domestic administration being in female hands in rooms 1 and 2 while room 4 on the opposite side of the street was associated with male activities as indicated by the martial and agricultural tools found inside.[9]
Also of interest amongst the finds is a jar with a painted scene at the top where two warriors fight surrounded by areas of cross-hatching (with a fruit tree). These areas may represent ploughed fields (and an orchard) and so be visual evidence for the territoriality of warfare in this era.[12]
Significance of the site
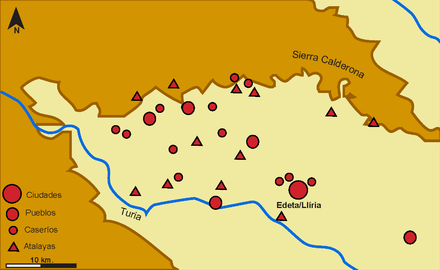
Owing to the small size of the site and lack of significant changes to the construction over two centuries, Bonet and Mata interpreted the site as dependent on Edeta and having a predominantly military function, to control the passes over, and mines within, the Sierra Calderona to the north.[13] Because Puntal dels Llops is built at a similar time to other fortified watchtowers (atalayas) surrounding Edeta, and is visually connected to these sites, they interpret all these sites as a planned defensive network to protect and control the territory of Edeta.[14] As such, the destruction or abandonment of these centres in the first decades of Roman occupation was an important element of the Roman strategy to suppress local control.[15]
This interpretation is not universally accepted, however. Other authors and even these same investigators have stressed the economic links between Puntal dels Llops (with its access to mountain and forest resources), and the agricultural villages and specialist artisans living on the plain.[16][17]
The current archaeological site
The site can be visited year-round. The Tourist Office in Olocau (Casa de la Señoría) has a small permanent collection of archaeological pieces from Puntal dels Llops and other nearby sites. Many of the most important objects excavated at Puntals dels Llops are now displayed in the Prehistory Museum of Valencia as part of their permanent collection on Iberian culture and Valencian prehistory in general.
Notes
- de Pedro 2002.
- Bonet & Mata 2002, pp. 213–217.
- Bonet & Mata 2002, pp. 33.
- Burillo 2001, p. 189.
- Bonet & Mata 2002, pp. 25-7.
- Bonet & Mata 2002, p. 18.
- Bonet & Mata 2002, pp. 218-9.
- Bonet & Mata 2002, pp. 152-3.
- Bonet & Mata 2016, pp. 40-1.
- Bonet & Mata 2002, pp. 219-20.
- Bonet & Mata 2002, pp. 210-11.
- González 2000, p. 332.
- Bonet & Mata 2002, pp. 214, 218.
- Bonet & Mata 2002, pp. 213-216.
- Bonet & Mata 2002, p. 217.
- Moret 1996, pp. 158-159.
- Bonet, Mata & Moreno 2008.
References
- Bonet, H.; Mata, C. (2002), El Puntal dels Llops: Un fortín edetano, Servicio de Investigación Prehistórica
- Bonet, H.; Mata, C. (2016), "Las cuentas claras: El rol de la mujer ibérica en la economía doméstica", in Delgado, A.; Picazo, M. (eds.), Los trabajos de las mujeres en el mundo antiguo: Cuidade y mantenimiento de la vida, Institut Català d'Arqueologia Clàssica, pp. 37–44
- Bonet, H.; Mata, C.; Moreno, A. (2008), "Iron age landscape and rural habitat in the edetan territory, Iberia (4th-3rd centuries BC)", Journal of Mediterranean Archaeology, 21:2, pp. 165–189
- Burillo, F. (2001), "Etnias y poblamiento en el área ibérico del valle medio del Ebro: Sedetanos e Edetanos", in Gardes, P.; Berrocal-Rangel, L. (eds.), Entre Celtas e Íberos: Las relaciones protohistóricas entre las Galias y Hispania, Rústica, pp. 187–200
- de Pedro, Ma. J. (2002), "El poblado de la Edad de Bronze", in Bonet, H.; Mata, C. (eds.), El Puntal dels Llops: Un fortín edetano, Servicio de Investigación Prehistórica, pp. 223–53
- Moret, P. (1996), Les fortifications ibériques: De la fin de l'âge du bronze à la conquête romaine, Casa de Velázquez
- González, R. (2000), "Aportación al estudio de los paisajes agrarios de la Edetania: Algunas consideraciones sobre la agricultura ibérica", in Olcina, M.; Soler, Jorge (eds.), Scripta en honerem Enrique A. Llobregat Conesa, Instituto Alicantino Juan Gil-Albert, pp. 325–340
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Puntal dels Llops. |
