Propionyl chloride
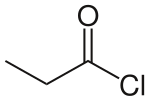
Propionyl chloride is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH2C(O)Cl. It is the acyl chloride derivative of propionic acid. It undergoes the characteristic reactions of acyl chlorides.[1] It is a colorless, corrosive, volatile liquid.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Propanoyl chloride | |
| Other names
Propionic chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.064 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H5ClO | |
| Molar mass | 92.52 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.0646 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −94 °C (−137 °F; 179 K) |
| Boiling point | 80 °C (176 °F; 353 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is used as a reagent for organic synthesis. In derived chiral amides and esters, the methylene protons are diastereotopic.[2]
References
- Michael B Smith (22 November 2016). Organic Synthesis. Elsevier Science. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-12-800807-2.
- Gage, James R.; Evans, David A. (1990). "Diastereoselective Aldol Condensation Using a Chiral Oxazolidinone Auxiliary: (2S,3S)-3-Hydroxy-3-phenyl-2-methylpropanoic Acid". Org. Synth. 68: 83. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.068.0083.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.