Polymethylhydrosiloxane
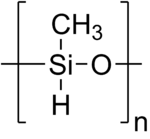
Polymethylhydrosiloxane (PMHS) is a polymer with the general structure -(CH3(H)Si-O)-. It is used in organic chemistry as a mild and stable reducing agent easily transferring hydrides to metal centers and a number of other reducible functional groups.[1] A variety of related materials are available under the following CAS registry numbers 9004-73-3, 16066-09-4, 63148-57-2, 178873-19-3. These include the tetramer ((MeSiHO)4), copolymers of dimethylsiloxane and methylhydrosiloxane, and trimethylsilyl terminated materials.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Methyl hydrogen siloxane; Poly(methyl siloxane); Poly(methylhydrosiloxane); Polysilicone 4 | |
| Identifiers | |
| Abbreviations | PMHS |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.119.568 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
| (CH3(H)SiO)n | |
| Molar mass | variable |
| Density | 1.06 g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
This material is prepared by the hydrolysis of methyldichlorosilane:
- n MeSiHCl2 + n H2O → (MeSiHO)n + 2n HCl
The related polymer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is made similarly, but lacking Si-H bonds, it exhibits no reducing properties.
Illustrative of its use, PMHS is used for in situ conversion of tributyltin oxide to tributyltin hydride:[2]
- 2"(MeSiH)" + (Bu3Sn)2O → "Me2Si2O" + 2 Bu3SnH
References
- J. M. Lavis, R. E. Maleczka, Jr. "Polymethylhydrosiloxane" Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2003, John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00062
- Jordi Tormo and Gregory C. Fu (2002). "Tributylstannane (Bu3SnH)-Catalyzed Barton-McCombie deoxygenation of Alcohols: 3-Deoxy-1,2:5,6-bis-O-(1-methylethyilidine)-α-D-ribo-hexafuranose". Organic Syntheses. 78: 239.
Further reading
- Larson, G. L.; Fry, J. L., "Ionic and organometallic-catalyzed organosilane reductions", Organic Reactions 2008, 71, 1-737. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or071.01