Poikilocytosis
Poikilocytosis is variation in cell shape: poikilocytes may be oval, teardrop-shaped, sickle-shaped or irregularly contracted.
| Poikilocytosis | |
|---|---|
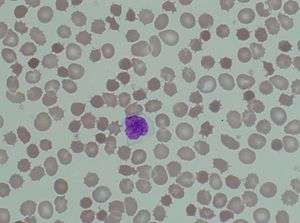 | |
| Acanthocytosis is one form of poikilocytosis |
Normal red blood cells are round, flattened disks that are thinner in the middle than at the edges. A poikilocyte is an abnormally shaped cell.[1] Generally, poikilocytosis can refer to an increase in abnormal red blood cells of any shape where they make up 10% or more of the total population.
Types
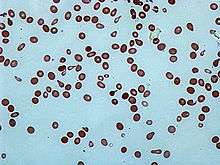
Membrane abnormalities
- Acanthocytes or Spur/Spike cells
- Codocytes or Target cells
- Echinocytes and Burr cells
- Elliptocytes and Ovalocytes
- Spherocytes
- Stomatocytes or Mouth cells
- Drepanocytes or Sickle Cells
- Degmacytes or "bite cells"
Trauma
- Dacrocytes or Teardrop Cells
- Keratocytes
- Microspherocytes and Pyropoikilocytes
- Schistocytes
- Semilunar bodies
Diagnosis
Poikilocytosis may be diagnosed during a test called a blood smear. During a blood smear, a medical technologist spreads a thin layer of blood on a microscope slide and stains the blood to help differentiate the cells. The technologist then views the blood under a microscope, where the sizes and shapes of the RBCs can be seen.
Treatment
In all cases, the treatment of poikilocytosis depends on its cause. For example, poikilocytosis can be caused by a vitamin deficiency (e.g. vitamin B12, folic acid), in which case the treatment is to replenish the deficient vitamin. It can be caused by a digestive disease, such as celiac disease, in which case the solution may lie in treating the underlying celiac disease so that nutrients can be properly absorbed.
Etymology
The term derives from poikilos (ποικίλος), which means "varied" in Ancient Greek.[2][3]
See also
References
- Barbara J. Bain (2006). Blood cells: a practical guide. Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 71–. ISBN 978-1-4051-4265-6. Retrieved 10 November 2010.
- (in Greek) Triantafyllidis Online Lexicon, ποικιλόθερμος, Retrieved on 2007-01-12
- "poikilo-". Wiktionary. Retrieved 14 October 2011.