Piperlongumine
Piperlongumine (PL) is a natural product constituent of the fruit of the long pepper (Piper longum),[1] a pepper plant found in southern India and southeast Asia.
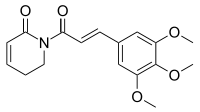 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-[(2E)-3-(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]-5,6-dihydropyridin-2(1H)-one | |
| Other names
Piplartine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.243.690 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H19NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 317.341 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Piperlongumine may have anti-cancer properties. In in vitro experiments, it selectively kills some types cancer cells over normal cells.[1] One study in a xenograft mouse model of cancer showed that piperlongumine inhibits the growth of malignant breast tumors and their associated metastases,[1][2] although this study has been retracted.[3] Its anticancer effects may be due to silencing the GSTP1 and/or the GSTO1 genes.[4][5] Piperlongumine inhibits the migration of breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231), an approach for discovering antimetastatic agents.[6] Piperlongumine has been shown to cause cytotoxicity in cancer cells via ferroptosis.[7]
Some piperlongumine derivatives are potent anti-inflammatory agents.[8] The synthesis typically involved a Schotten-Baumann reaction between the acid chloride of 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamic acid with the corresponding amines. Wang et al., evaluated piperlongumine as a novel senolytic agent.[9]
References
- Raj, Lakshmi; Ide, Takao; Gurkar, Aditi U.; Foley, Michael; Schenone, Monica; Li, Xiaoyu; Tolliday, Nicola J.; Golub, Todd R.; et al. (2011). "Selective killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targeting the stress response to ROS". Nature. 475 (7355): 231–234. doi:10.1038/nature10167. PMC 3316487. PMID 21753854.
- "Novel Compound Selectively Kills Cancer Cells by Blocking Their Response to Oxidative Stress". ScienceDaily. July 2011.
- Raj, Lakshmi; Ide, Takao; Gurkar, Aditi U.; Foley, Michael; Schenone, Monica; Li, Xiaoyu; Tolliday, Nicola J.; Golub, Todd R.; Carr, Steven A.; Shamji, Alykhan F.; Stern, Andrew M.; Mandinova, Anna; Schreiber, Stuart L.; Lee, Sam W. (2018). "Retraction Note: Selective killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targeting the stress response to ROS". Nature. 561 (7723): 420. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0284-y. PMC 6148382. PMID 30046103.
- Researchers uncover mechanism for cancer-killing properties of pepper plant reporting on Structural and Biochemical Analyses Reveal the Mechanism of Glutathione S-Transferase Pi 1 Inhibition by the Anti-cancer Compound Piperlongumine. 2017
- Li, L; Zhao, Y.; Cao, R.; Lin, L.; Cai, G.; Li, J.; Qi, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z. Activity-based protein profiling reveals GSTO1 as the covalent target of piperlongumine and a promising target for combination therapy for cancer. Chem. Commun, 55 (2019) 4407 - 4410
- Valli, M.; Altei, W.; dos Santos, R.; De Lucca Jr., E.; Dessoy, M.; Pioli, R.; Cotinguiba, F.; Cachet, X.; Michel, S.; Furlan, M.; Dias, L.; Andricopulo, A.; Bolzani, V. Synthetic Analogue of the Natural Product Piperlongumine as a Potent Inhibitor of Breast Cancer Cell Line Migration. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, v. 28, p. 475-484, 2017.https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20160303
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Kasukabe, T.; Kumakura, S. Piperlongumine rapidly induces the death of human pancreatic cancer cells mainly through the induction of ferroptosis. International Journal of Oncology 52 (2018) 1011 - 1022
- Seo, Young Hwa; Kim, Jin-Kyung; Jun, Jong-Gab (2014). "Synthesis and biological evaluation of piperlongumine derivatives as potent anti-inflammatory agents". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 24 (24): 5727–5730. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.10.054. ISSN 0960-894X. PMID 25453809.
- Wang, Y.; Chang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, G. (2016). "Discovery of piperlongumine as a potential novel lead for the development of senolytic agents". Aging. 8 (11): 2915–2926. doi:10.18632/aging.101100. PMC 5191878. PMID 27913811.