Pinus echinata
Pinus echinata, the shortleaf pine,[2] is a species of pine native to the eastern United States from southernmost New York, south to northern Florida, west to eastern Oklahoma, and southwest to eastern Texas. The tree is variable in form, sometimes straight, sometimes crooked, with an irregular crown. This tree reaches heights of 20–30 metres (65–100 ft) with a trunk diameter of 0.5–0.9 metres (1 ft 8 in–2 ft 11 in).
| Shortleaf pine | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Shortleaf Pine forest | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Pinaceae |
| Genus: | Pinus |
| Subgenus: | P. subg. Pinus |
| Section: | P. sect. Trifoliae |
| Subsection: | P. subsect. Australes |
| Species: | P. echinata |
| Binomial name | |
| Pinus echinata | |
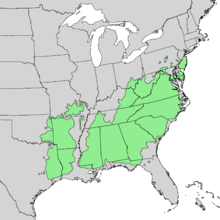 | |
| Natural range | |
The leaves are needle-like, in fascicles (bundles) of two and three mixed together, and from 7–11 cm (2 3⁄4–4 1⁄4 in) long. The cones are 4–7 cm (1 1⁄2–2 3⁄4 in) long, with thin scales with a transverse keel and a short prickle. They open at maturity but are persistent.[3] Shortleaf pine seedlings develop a persistent J-shaped crook near the ground surface.[4] Axillary and other buds form near the crook and initiate growth if the upper stem is killed by fire or is severed.
This pine is a source of wood pulp, plywood veneer, and lumber for a variety of uses. The shortleaf pine is one of the southern US "southern yellow pines; it is also occasionally called southern yellow pine or the shortstraw pine. Shortleaf pine has the largest range of the southern US yellow pines.

This pine occupies a variety of habitats from rocky uplands to wet flood plains. It frequently hybridizes naturally with loblolly pine and pitch pine where their ranges intersect.
References
- Farjon, A. (2013). "Pinus echinata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2013: e.T42359A2974993. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T42359A2974993.en. Archived from the original on 2018-06-02.
- "Pinus echinata". Natural Resources Conservation Service PLANTS Database. USDA. Retrieved 4 October 2015.
- Kral, Robert (1993). "Pinus echinata". In Flora of North America Editorial Committee (ed.). Flora of North America North of Mexico (FNA). 2. New York and Oxford – via eFloras.org, Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA.
- Lawson, Edwin R. (1990). "Pinus echinata". In Burns, Russell M.; Honkala, Barbara H. (eds.). Conifers. Silvics of North America. Washington, D.C.: United States Forest Service (USFS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). 1 – via Southern Research Station (www.srs.fs.fed.us).
- "Silvics of Shortleaf Pine" (PDF). North Carolina Forest Service. January 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-12-24. Retrieved 11 November 2018.
External links

- Gymnosperm Database: Pinus echinata
- NCRS: USDA Plants Profile: Pinus echinata
