Phthalimide
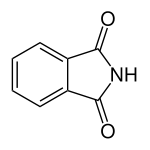
Phthalimide is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2NH. It is the imide derivative of phthalic anhydride. It is a sublimable white solid that is slightly soluble in water but more so upon addition of base. It is used as a precursor to other organic compounds as a masked source of ammonia.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Isoindole-1,3-dione | |
| Other names
1,3-dioxoisoindoline Phthalimidoyl (deprotonated) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.458 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C8H5NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 147.133 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 238 °C (460 °F; 511 K) |
| Boiling point | 336 °C (637 °F; 609 K) sublimes |
| <0.1 g/100 ml (19.5 °C) | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 8.3 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 5.7 |
| −78.4×10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Related compounds | |
Related Amides |
Maleimide |
Related compounds |
Phthalic anhydride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation
Phthalimide can be prepared by heating phthalic anhydride with alcoholic ammonia giving 95–97% yield. Alternatively, it may be prepared by treating the anhydride with ammonium carbonate or urea. It can also be produced by ammoxidation of o-xylene.[2]
Uses
Phthalimide is used as a precursor to anthranilic acid, a precursor to azo dyes and saccharin.[2]
Alkyl phthalimides are useful precursors to amines in chemical synthesis, especially in peptide synthesis where they are used "to block both hydrogens and avoid racemization of the substrates".[3] Alkyl halides can be converted to the N-alkylphthalimide:
- C6H4(CO)2NH + RX + NaOH → C6H4(CO)2NR + NaX + H2O
The amine is commonly liberated using hydrazine:
- C6H4(CO)2NR + N2H4 → C6H4(CO)2N2H2 + RNH2
Dimethylamine can also be used.[4]
Some examples of phthalimide drugs include thalidomide, amphotalide, taltrimide and talmetoprim. With a trichloromethylthio substituent, a phthalimide-derived fungicide is Folpet.
Reactivity
It forms salts upon treatment with bases such as sodium hydroxide. The high acidity of the imido N-H is the result of the pair of flanking electrophilic carbonyl groups. Potassium phthalimide, made by reacting phthalimide with potassium carbonate in water at 100 °C or with potassium hydroxide in absolute ethanol,[5] is used in the Gabriel synthesis of primary amines, such as glycine.
Natural occurrence
Kladnoite is a natural mineral analog of phthalimide.[6] It is very rarely found among a few burning coal fire sites.
Safety
Phthalimide has low acute toxicity with LD50 (rat, oral) of greater than 5,000 mg/kg.[2]
References
- "Phthalimide". Chemicalland21. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- Lorz, Peter M.; Towae, Friedrich K.; Enke, Walter; Jäckh, Rudolf; Bhargava, Naresh; Hillesheim, Wolfgang. "Phthalic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_181.pub2.
- "Phthalimides". Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- "Deprotection – removal of amine protecting groups (phthalimide and dimethylaminosulphonyl)". Archived from the original on 2014-12-03. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- Salzberg, P. L.; Supniewski, J. V. "β-Bromoethylphthalimide". Organic Syntheses. 7: 8. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.007.0008.; Collective Volume, 1, p. 119
- "Kladnoite". mindat.org. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
General reading
- Vollhardt, K. Peter C.; Schore, Neil Eric (2002). Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function (4th ed.). New York: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-4374-3.
- Finar, Ivor Lionel (1973). Organic Chemistry. 1 (6th ed.). London: Longman. ISBN 0-582-44221-4.