Photometric stereo
Photometric stereo is a technique in computer vision for estimating the surface normals of objects by observing that object under different lighting conditions. It is based on the fact that the amount of light reflected by a surface is dependent on the orientation of the surface in relation to the light source and the observer.[1] By measuring the amount of light reflected into a camera, the space of possible surface orientations is limited. Given enough light sources from different angles, the surface orientation may be constrained to a single orientation or even overconstrained.
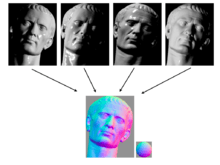
The technique was originally introduced by Woodham in 1980.[2] The special case where the data is a single image is known as shape from shading, and was analyzed by B. K. P. Horn in 1989.[3] Photometric stereo has since been generalized to many other situations, including extended light sources and non-Lambertian surface finishes. Current research aims to make the method work in the presence of projected shadows, highlights, and non-uniform lighting.
Basic Method
Under Woodham's original assumptions — Lambertian reflectance, known point-like distant light sources, and uniform albedo — the problem can be solved by inverting the linear equation , where is a (known) vector of observed intensities, is the (unknown) surface normal, and is a (known) matrix of normalized light directions.
This model can easily be extended to surfaces with non-uniform albedo, while keeping the problem linear.[4] Taking an albedo reflectivity of , the formula for the reflected light intensity becomes:
If is square (there are exactly 3 lights) and non-singular, it can be inverted, giving:
Since the normal vector is known to have length 1, must be the length of the vector , and is the normalised direction of that vector. If is not square (there are more than 3 lights), a generalisation of the inverse can be obtained using the Moore-Penrose pseudoinverse,[5] by simply multiplying both sides with giving:
After which the normal vector and albedo can be solved as described above.
Non-Lambertian surfaces
The classical photometric stereo problem concerns itself only with Lambertian surfaces, with perfectly diffuse reflection. This is unrealistic for many types of materials, especially metals, glass and smooth plastics, and will lead to aberrations in the resulting normal vectors.
Many methods have been developed to lift this assumption. In this section, a few of these are listed.
Specular reflections
Historically, in computer graphics, the commonly used model to render surfaces started with Lambertian surfaces and progressed first to include simple specular reflections. Computer vision followed a similar course with photometric stereo. Specular reflections were among the first deviations from the Lambertian model. These are a few adaptations that have been developed.
- Many techniques ultimately rely on modelling the reflectance function of the surface, that is, how much light is reflected in each direction.[6] This reflectance function has to be invertible. The reflected light intensities towards the camera is measured, and the inverse reflectance function is fit onto the measured intensities, resulting in a unique solution for the normal vector.
General BRDFs and beyond
According to the Bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) model, a surface may distribute the amount of light it receives in any outward direction. This is the most general known model for opaque surfaces. Some techniques have been developed to model (almost) general BRDFs. In practice, all of these require many light sources to obtain reliable data. These are methods in which surfaces with general BRDFs can be measured.
- Determine the explicit BRDF prior to scanning.[7] To do this, a different surface is required that has the same or a very similar BRDF, of which the actual geometry (or at least the normal vectors for many points on the surface) is already known.[8] The lights are then individually shone upon the known surface, and the amount of reflection into the camera is measured. Using this information, a look-up table can be created that maps reflected intensities for each light source to a list of possible normal vectors. This puts constraints on the possible normal vectors the surface may have, and reduces the photometric stereo problem to an interpolation between measurements. Typical known surfaces to calibrate the look-up table with are spheres for their wide variety of surface orientations.
- Restricting the BRDF to be symmetrical.[9] If the BRDF is symmetrical, the direction of the light can be restricted to a cone about the direction to the camera. Which cone this is depends on the BRDF itself, the normal vector of the surface, and the measured intensity. Given enough measured intensities and the resulting light directions, these cones can be approximated and therefore the normal vectors of the surface.
Some progress has been made towards modelling an even more general surfaces, such as Spatially Varying Bidirectional Distribution Functions (SVBRDF), Bidirectional surface scattering reflectance distribution functions (BSSRDF), and accounting for interreflections.[10][11] However, such methods are still fairly restrictive in photometric stereo. Better results have been achieved with structured light.[12]
See also
- Photometry
- Stereo vision
- 3D scanner
References
- Ying Wu. "Radiometry, BRDF and Photometric Stereo" (PDF). Northwestern University. Retrieved 2015-03-25.
- Woodham, R.J. 1980. Photometric method for determining surface orientation from multiple images. Optical Engineerings 19, I, 139-144.
- B. K. P. Horn, 1989. Obtaining shape from shading information. In B. K. P. Horn and M. J. Brooks, eds., Shape from Shading, pages 121–171. MIT Press.
- S. Barsky and Maria Petrou, 2003. The 4-source photometric stereo technique for 3-dimensional surfaces in the presence of highlights and shadows. In IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 25, issue 10, pages 1239-1252. IEEE.
- Chaman Singh Verma and Mon-Ju Wu. "Photometric Stereo". University of Wisconsin-Madison. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- Hemant D. Tagare and Rui J.P. de Figueiredo, 1991. A Theory of Photometric Stereo for a Class of Diffuse Non-Lambertian Surfaces. In IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 13, no. 2. IEEE.
- Katsushi Ikeuchi, 1981. Determining Surface Orientations of Specular Surfaces by Using the Photometric Stereo Method. In IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. PAMI-3, issue 6, pages 661-669. IEEE.
- Aaron Hertzmann and Steven M. Seitz, 2005. Example-Based Photometric Stereo: Shape Reconstruction with General, Verying BRDFs. In IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 27, no. 8. IEEE.
- Michael Holroyd, Jason Lawrence, Greg Humphreys and Todd Zickler, 2008. A Photometric Approach for Estimating Normals and Tangents. In ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2008 Papers, pages 133:1-133:9. ACM.
- Shree K. Nayar, Katsushi Ikeuchi and Takeo Kanade, 1991. Shape from interreflections. In International Journal of Computer Vision, vol. 6, number 3, pages 173-195.
- Miao Liao, Xinyu Huang and Ruigang Yang, 2011. Interreflection Removal for Photometric Stereo by Using Spectrum-dependent Albedo. In 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 689-696. IEEE.
- Tongbo Chen, Hendrik Lensch, Christian Fuchs and H.P. Seidel, 2007. Polarization and Phase-shifting for 3D Scanning of Translucent Objects. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2007, pages 1-8. IEEE.