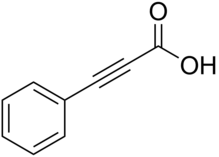
Phenylpropiolic acid
Phenylpropiolic acid, C6H5CCCO2H, formed by the action of alcoholic potash on cinnamic acid dibromide, C6H5CHBrCHBrCO2H, crystallizes in long needles or prisms which melt at 136–137 °C. When heated with water to 120 °C, it yields phenylacetylene (C6H5CCH). Chromic acid oxidizes it to benzoic acid; zinc and acetic acid reduce it to cinnamic acid, C6H5CH=CHCO2H, whilst sodium amalgam reduces it to hydrocinnamic acid, C6H5CH2CH2CO2H. Ortho-nitrophenylpropiolic acid, NO2C6H4CCCO2H, prepared by the action of alcoholic potash on ortho-nitrocinnamic acid dibromide, crystallizes in needles which decompose when heated to 155–156 °C. It is readily converted into indigo.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Phenylpropynoic acid | |
| Other names
Phenylpropiolic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.260 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 146.14 g/mol |
| Melting point | 135 to 137 °C (275 to 279 °F; 408 to 410 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
-

This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.