Peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase
Peptidyl-glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of glycine amides to amides and glyoxylate.
The enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of many signaling peptides and some fatty acid amides.[5]
In humans, the enzyme is encoded by the PAM gene.[6][7] This transformation is achieved by conversion of a prohormone to the corresponding amide (C(O)NH2). This enzyme is the only known pathway for generating peptide amides, which renders the peptide more hydrophilic.[8]
Function
This gene encodes a multifunctional protein. It has two enzymatically active domains with catalytic activities - peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) and peptidyl-alpha-hydroxyglycine alpha-amidating lyase (PAL). These catalytic domains work sequentially to catalyze neuroendocrine peptides to active alpha-amidated products. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene, but some of their full-length sequences are not yet known.[7]
The PHM subunit effects hydroxylation of an O-terminal glycine residue:
- peptide-C(O)NHCH2CO2− + O2 + 2 [H] → peptide-C(O)NHCH(OH)CO2− + H2O
Involving hydroxylation of a hydrocarbon by O2, this process relies on a copper cofactor. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase, also a copper-containing enzyme, effects a similar transformation.[9]
The PAL subunit then completes the conversion, by catalyzing elimination from the hydroxylated glycine:
- peptide-C(O)NHCH(OH)CO2− → peptide-C(O)NH2 + CH(O)CO2−
The eliminated coproduct is glyoxylate, written above as CH(O)CO2−.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000145730 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026335 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- . doi:10.1021/bi982255j. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - Glauder J, Ragg H, Rauch J, Engels JW (Jul 1990). "Human peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase: cDNA, cloning and functional expression of a truncated form in COS cells". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 169 (2): 551–8. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(90)90366-U. PMID 2357221.
- "Entrez Gene: PAM peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase".
- Eipper BA, Milgram SL, Husten EJ, Yun HY, Mains RE (1993). "Peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase: a multifunctional protein with catalytic, processing, and routing domains". Protein Sci. 2 (4): 489–97. doi:10.1002/pro.5560020401. PMC 2142366. PMID 8518727.
- . doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.558494. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help)
Further reading
- Pittner RA, Albrandt K, Beaumont K, Gaeta LS, Koda JE, Moore CX, Rittenhouse J, Rink TJ (1994). "Molecular physiology of amylin". J. Cell. Biochem. 55 Suppl (S1994A): 19–28. doi:10.1002/jcb.240550004. PMID 7929615.
- Ouafik LH, Stoffers DA, Campbell TA, Johnson RC, Bloomquist BT, Mains RE, Eipper BA (1992). "The multifunctional peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase gene: exon/intron organization of catalytic, processing, and routing domains". Mol. Endocrinol. 6 (10): 1571–84. doi:10.1210/me.6.10.1571. PMID 1448112.
- Maltese JY, Eipper BA (1993). "Developmental expression of peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PAM) in primary cultures of neonatal rat cardiocytes: a model for studying regulation of PAM expression in the rat heart". Mol. Endocrinol. 6 (12): 1998–2008. doi:10.1210/me.6.12.1998. PMID 1491686.
- Braas KM, Harakall SA, Ouafik L, Eipper BA, May V (1992). "Expression of peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase: an in situ hybridization and immunocytochemical study". Endocrinology. 130 (5): 2778–88. doi:10.1210/en.130.5.2778. PMID 1572293.
- Roberts AN, Leighton B, Todd JA, Cockburn D, Schofield PN, Sutton R, Holt S, Boyd Y, Day AJ, Foot EA (1990). "Molecular and functional characterization of amylin, a peptide associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86 (24): 9662–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.24.9662. PMC 298561. PMID 2690069.
- Vos MD, Jones JE, Treston AM (1995). "Human peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase transcripts derived by alternative mRNA splicing of an unreported exon". Gene. 163 (2): 307–11. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00364-C. PMID 7590286.
- Tsukamoto T, Noguchi M, Kayama H, Watanabe T, Asoh T, Yamamoto T (1995). "Increased peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase activity in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis". Intern. Med. 34 (4): 229–32. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.34.229. PMID 7606087.
- Yun HY, Johnson RC, Mains RE, Eipper BA (1993). "Topological switching of the COOH-terminal domain of peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase by alternative RNA splicing". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 301 (1): 77–84. doi:10.1006/abbi.1993.1117. PMID 7680192.
- Mains RE, Milgram SL, Keutmann HT, Eipper BA (1995). "The NH2-terminal proregion of peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase facilitates the secretion of soluble proteins". Mol. Endocrinol. 9 (1): 3–13. doi:10.1210/me.9.1.3. PMID 7760848.
- Tateishi K, Arakawa F, Misumi Y, Treston AM, Vos M, Matsuoka Y (1995). "Isolation and functional expression of human pancreatic peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 205 (1): 282–90. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1994.2662. PMID 7999037.
- Martínez A, Montuenga LM, Springall DR, Treston A, Cuttitta F, Polak JM (1993). "Immunocytochemical localization of peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase enzymes (PAM) in human endocrine pancreas". J. Histochem. Cytochem. 41 (3): 375–80. doi:10.1177/41.3.8094086. PMID 8094086.
- Kapuscinski M, Green M, Sinha SN, Shepherd JJ, Shulkes A (1993). "Peptide alpha-amidation activity in human plasma: relationship to gastrin processing". Clin. Endocrinol. 39 (1): 51–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.1993.tb01750.x. PMID 8102327.
- Yun HY, Keutmann HT, Eipper BA (1994). "Alternative splicing governs sulfation of tyrosine or oligosaccharide on peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (14): 10946–55. PMID 8144680.
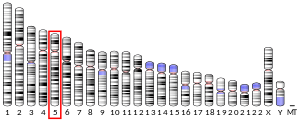
- Ouafik LH, Mattei MG, Giraud P, Oliver C, Eipper BA, Mains RE (1994). "Localization of the gene encoding peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PAM) to human chromosome 5q14-5q21". Genomics. 18 (2): 319–21. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1471. PMID 8288234.
- Husten EJ, Tausk FA, Keutmann HT, Eipper BA (1993). "Use of endoproteases to identify catalytic domains, linker regions, and functional interactions in soluble peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (13): 9709–17. PMID 8486658.
- Yun HY, Milgram SL, Keutmann HT, Eipper BA (1996). "Phosphorylation of the cytosolic domain of peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (50): 30075–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.50.30075. PMID 8530412.
- Morris KM, Cao F, Onagi H, Altamore TM, Gamble AB, Easton CJ (1 December 2012). "Prohormone-substrate peptide sequence recognition by peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase and its reflection in increased glycolate inhibitor potency". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 22 (23): 7015–7018. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.10.004. PMID 23084901.