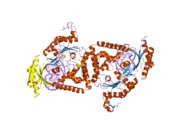POLK
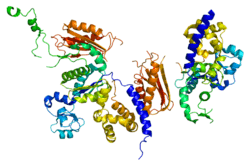
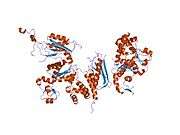
DNA polymerase kappa is an DNA polymerase that in humans is encoded by the POLK gene. It is involved in translesion synthesis.[4][5][6]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000122008 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Ohashi E, Ogi T, Kusumoto R, Iwai S, Masutani C, Hanaoka F, Ohmori H (Aug 2000). "Error-prone bypass of certain DNA lesions by the human DNA polymerase κ". Genes Dev. 14 (13): 1589–94. doi:10.1101/gad.14.13.1589. PMC 316741. PMID 10887153.
- Gerlach VL, Aravind L, Gotway G, Schultz RA, Koonin EV, Friedberg EC (Nov 1999). "Human and mouse homologs of Escherichia coli DinB (DNA polymerase IV), members of the UmuC/DinB superfamily". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 96 (21): 11922–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.21.11922. PMC 18388. PMID 10518552.
- "Entrez Gene: POLK Polymerase (DNA directed) kappa".
Further reading
- Bavoux C, Hoffmann JS, Cazaux C (2005). "Adaptation to DNA damage and stimulation of genetic instability: the double-edged sword mammalian DNA polymerase kappa". Biochimie. 87 (7): 637–46. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2005.02.007. PMID 15989980.
- Ogi T, Kato T, Kato T, Ohmori H (2000). "Mutation enhancement by DINB1, a mammalian homologue of the Escherichia coli mutagenesis protein dinB". Genes Cells. 4 (11): 607–18. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2443.1999.00289.x. PMID 10620008.
- Johnson RE, Prakash S, Prakash L (2000). "The human DINB1 gene encodes the DNA polymerase Polθ". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (8): 3838–43. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.8.3838. PMC 18103. PMID 10760255.
- Gerlach VL, Feaver WJ, Fischhaber PL, Friedberg EC (2001). "Purification and characterization of pol kappa, a DNA polymerase encoded by the human DINB1 gene". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (1): 92–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004413200. PMID 11024016.
- Haracska L, Unk I, Johnson RE, et al. (2002). "Stimulation of DNA Synthesis Activity of Human DNA Polymerase κ by PCNA". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (3): 784–91. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.3.784-791.2002. PMC 133560. PMID 11784855.
- Washington MT, Johnson RE, Prakash L, Prakash S (2002). "Human DINB1-encoded DNA polymerase κ is a promiscuous extender of mispaired primer termini". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (4): 1910–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.032594399. PMC 122293. PMID 11842189.
- Suzuki N, Ohashi E, Kolbanovskiy A, et al. (2002). "Translesion synthesis by human DNA polymerase kappa on a DNA template containing a single stereoisomer of dG-(+)- or dG-(−)-anti-N(2)-BPDE (7,8-dihydroxy-anti-9,10-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene)". Biochemistry. 41 (19): 6100–6. doi:10.1021/bi020049c. PMID 11994005.
- Fischhaber PL, Gerlach VL, Feaver WJ, et al. (2002). "Human DNA polymerase kappa bypasses and extends beyond thymine glycols during translesion synthesis in vitro, preferentially incorporating correct nucleotides". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (40): 37604–11. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206027200. PMID 12145297.
- Bergoglio V, Bavoux C, Verbiest V, et al. (2003). "Localisation of human DNA polymerase kappa to replication foci". J. Cell Sci. 115 (Pt 23): 4413–8. doi:10.1242/jcs.00162. PMID 12414988.
- Haracska L, Prakash L, Prakash S (2003). "Role of human DNA polymerase κ as an extender in translesion synthesis". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (25): 16000–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.252524999. PMC 138554. PMID 12444249.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Wolfle WT, Washington MT, Prakash L, Prakash S (2003). "Human DNA polymerase κ uses template–primer misalignment as a novel means for extending mispaired termini and for generating single-base deletions". Genes Dev. 17 (17): 2191–9. doi:10.1101/gad.1108603. PMC 196459. PMID 12952891.
- Haracska L, Prakash L, Prakash S (2003). "A mechanism for the exclusion of low-fidelity human Y-family DNA polymerases from base excision repair". Genes Dev. 17 (22): 2777–85. doi:10.1101/gad.1146103. PMC 280626. PMID 14630940.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Suzuki N, Itoh S, Poon K, et al. (2004). "Translesion synthesis past estrogen-derived DNA adducts by human DNA polymerases eta and kappa". Biochemistry. 43 (20): 6304–11. doi:10.1021/bi0360298. PMID 15147214.
- Ohashi E, Murakumo Y, Kanjo N, et al. (2005). "Interaction of hREV1 with three human Y-family DNA polymerases". Genes Cells. 9 (6): 523–31. doi:10.1111/j.1356-9597.2004.00747.x. PMID 15189446.
- Washington MT, Minko IG, Johnson RE, et al. (2004). "Efficient and Error-Free Replication Past a Minor-Groove DNA Adduct by the Sequential Action of Human DNA Polymerases ι and κ". Mol. Cell. Biol. 24 (13): 5687–93. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.13.5687-5693.2004. PMC 480884. PMID 15199127.
- Uljon SN, Johnson RE, Edwards TA, et al. (2005). "Crystal structure of the catalytic core of human DNA polymerase kappa". Structure. 12 (8): 1395–404. doi:10.1016/j.str.2004.05.011. PMID 15296733.
External links
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: Q9UBT6 (DNA polymerase kappa) at the PDBe-KB.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.