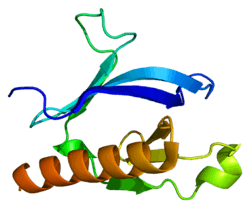PLEKHA1
Pleckstrin homology domain-containing family A member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PLEKHA1 gene.[5][6][7]
Interactions
PLEKHA1 has been shown to interact with MPDZ.[8]
gollark: > That's not how the Judeo-Christian God behaves.Really? Said god seems to really like being mean for no good reason.
gollark: Well, see, people doing that often get bored and decide to use their not-very-godlike powers to wreak havoc upon the simulated people.
gollark: Have you never played the sims or something?
gollark: Planning the next disaster.
gollark: Not the Judaic (is that even an adjective) one.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000107679 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000040268 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Dowler S, Currie RA, Campbell DG, Deak M, Kular G, Downes CP, Alessi DR (Jan 2001). "Identification of pleckstrin-homology-domain-containing proteins with novel phosphoinositide-binding specificities". Biochem J. 351 (Pt 1): 19–31. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3510019. PMC 1221362. PMID 11001876.
- Hogan A, Yakubchyk Y, Chabot J, Obagi C, Daher E, Maekawa K, Gee SH (Dec 2004). "The phosphoinositol 3,4-bisphosphate-binding protein TAPP1 interacts with syntrophins and regulates actin cytoskeletal organization". J Biol Chem. 279 (51): 53717–24. doi:10.1074/jbc.M410654200. PMID 15485858.
- "Entrez Gene: PLEKHA1 pleckstrin homology domain containing, family A (phosphoinositide binding specific) member 1".
- Kimber WA, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Cheung PC, Deak M, Marsden LJ, Kieloch A, Watt S, Javier RT, Gray A, Downes CP, Lucocq JM, Alessi DR (Feb 2002). "Evidence that the tandem-pleckstrin-homology-domain-containing protein TAPP1 interacts with Ptd(3,4)P2 and the multi-PDZ-domain-containing protein MUPP1 in vivo". Biochem. J. 361 (Pt 3): 525–36. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3610525. PMC 1222335. PMID 11802782.
Further reading
- Thomas CC, Dowler S, Deak M, Alessi DR, van Aalten DM (2001). "Crystal structure of the phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate-binding pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of tandem PH-domain-containing protein 1 (TAPP1): molecular basis of lipid specificity". Biochem. J. 358 (Pt 2): 287–94. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3580287. PMC 1222060. PMID 11513726.
- Kimber WA, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Cheung PC, Deak M, Marsden LJ, Kieloch A, Watt S, Javier RT, Gray A, Downes CP, Lucocq JM, Alessi DR (2002). "Evidence that the tandem-pleckstrin-homology-domain-containing protein TAPP1 interacts with Ptd(3,4)P2 and the multi-PDZ-domain-containing protein MUPP1 in vivo". Biochem. J. 361 (Pt 3): 525–36. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3610525. PMC 1222335. PMID 11802782.
- Marshall AJ, Krahn AK, Ma K, Duronio V, Hou S (2002). "TAPP1 and TAPP2 Are Targets of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Signaling in B Cells: Sustained Plasma Membrane Recruitment Triggered by the B-Cell Antigen Receptor". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (15): 5479–91. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.15.5479-5491.2002. PMC 133950. PMID 12101241.
- Kimber WA, Deak M, Prescott AR, Alessi DR (2003). "Interaction of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPL1 with the PtdIns(3,4)P2-binding adaptor protein TAPP1". Biochem. J. 376 (Pt 2): 525–35. doi:10.1042/BJ20031154. PMC 1223793. PMID 14516276.
- Jakobsdottir J, Conley YP, Weeks DE, Mah TS, Ferrell RE, Gorin MB (2006). "Susceptibility Genes for Age-Related Maculopathy on Chromosome 10q26". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 77 (3): 389–407. doi:10.1086/444437. PMC 1226205. PMID 16080115.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.