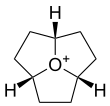
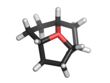
Oxatriquinane
Oxatriquinane (oxoniaperhydrotriquinacene[1]) is an alkyl oxonium ion with formula C
9H
15O+
, remarkable for being stable in aqueous solution. It has a cyclononane backbone, with a trivalent oxygen connected to carbon 1, 4, and 7, forming three fused pentagonal rings.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2as,4as,6as)-Octahydro-1H-2a1-oxacyclopenta[cd]pentalen-2a1-ium | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C9H15O | |||
| Molar mass | 139.218 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
History
Oxatriquinane was first described in 2008, and was obtained after a five-step synthesis starting from 1,4,7-cyclononatriene.[2][3][4] At the time it had the longest C–O bond lengths (1.54 Å, C–O bonds in ethers are generally ~1.43 Å) and most acute C−O−C angles ever observed in a compound.[2]
Reactions
Oxonium ions normally are strong alkylating agents and are only observed in solution as reactive intermediates or under extreme conditions. Oxatriquinane is an exception: it does not react with boiling water or with alcohols, thiols, halide ions, or amines, although it does react with stronger nucleophiles such as hydroxide, cyanide, and azide.[2] The ability of the oxygen to enter into a fourth covalent bond has been of some theoretical interest and was achieved using carborane acid.[5]
Analogues
Related species include oxatriquinacene,[2] the tri-unsaturated analogue, which is of interest as a possible precursor to oxaacepentalene, a neutral aromatic species. 1,4,7-tri-tert-butyloxatriquinane has also been synthesised; this compound contains significant amounts of intramolecular steric strain, resulting in further bond elongation to give C–O bond lengths of 1.622 Å, the longest recorded in any species.[6]
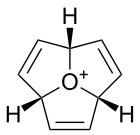 Oxatriquinacene
Oxatriquinacene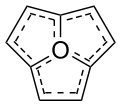 Oxaacepentalene
Oxaacepentalene
References
- Triquinane is more often used in the natural product literature to refer to three angularly fused cyclopentane rings sharing a common quaternary carbon in the center, a structure which contains one more carbon atom at the periphery. Moreover, substitution by O+ is more properly designated by the prefix oxonia. Nevertheless, the authors who first prepared the cation called it oxatriquinane, and the name has been perpetuated in the literature. A semisystematic name in line with standard nomenclature might be 2a1-oxonia-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydroquinacene.
- Mark Mascal; Nema Hafezi; Nabin K. Meher & James C. Fettinger (2008). "Oxatriquinane and Oxatriquinacene: Extraordinary Oxonium Ions". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 130 (41): 13532–13533. doi:10.1021/ja805686u. PMID 18798616.
- Rachel Petkewich (September 29, 2008). "Taming Alkyl Oxonium Ions: Fused tricyclic structure stabilizes famously reactive alkylating agents". Chemical and Engineering News. 86 (39): 10. doi:10.1021/cen-v086n039.p010.
- Tim Reid (3 October 2008). "Oxonium ions: Ring of stability". Nature Chemistry. doi:10.1038/nchem.70.
- Stoyanov, Evgenii S.; Gunbas, Gorkem; Hafezi, Nema; Mascal, Mark; Stoyanova, Irini V.; Tham, Fook S.; Reed, Christopher A. (11 January 2012). "The R3O+···H+ Hydrogen Bond: Toward a Tetracoordinate Oxadionium(2+) Ion". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 134 (1): 707–714. doi:10.1021/ja209942s. PMC 3257418. PMID 22133059.
- Gunbas, Gorkem; Hafezi, Nema; Sheppard, William L.; Olmstead, Marilyn M.; Stoyanova, Irini V.; Tham, Fook S.; Meyer, Matthew P.; Mascal, Mark (18 November 2012). "Extreme oxatriquinanes and a record C–O bond length". Nature Chemistry. 4 (12): 1018–1023. Bibcode:2012NatCh...4.1018G. doi:10.1038/nchem.1502. PMID 23174982.