Ouster (company)
Ouster is a lidar technology company based in San Francisco, it builds high-resolution 3D lidar sensors for use in autonomous vehicles, robotics, drones, mapping, mining, defense and more.[3][4][5][6] Its sensors produce camera-like images from ambient infrared, with software-focused mapping that reduces the need for high precision GPS systems, wheel odometry or gyroscopes.[7][8]
| Private | |
| Industry | Lidar |
| Founded | 2015 |
| Headquarters | San Francisco, California, United States |
Key people | |
| Products | Lidar |
Number of employees | 125[2] (2019) |
| Website | ouster |
History
Angus Pacala and Mark Frichtl founded Ouster in 2015, along with two other former Stanford University classmates, after working at laser-based sensing company Quanergy.[9]
Ouster launched out of stealth in December 2017, and in 2019 it raised an additional $60 million in funding following a $27 million series A. The latter round — which was led by Runway Growth Capital, with contributions from Silicon Valley Bank, Cox Enterprises, Constellation Tech Ventures, Fontinalis Partners, Carthona Capital, and others — brought the company’s total raised to $90 million.[10][11][12]
Operations
Ouster has gained more than 700 design wins across 15 different industries in 50 countries;[13] the company expanded its business to Europe and Asia in 2019, opening new offices in Paris, Shanghai and Hong Kong. Its sensors are on Postmates’ robots in sidewalks of Los Angeles, Kodiak’s trucks on the highways of Texas, and on drones in the DARPA SubT challenge coal mines of Pennsylvania in 2019.[14][15][16]
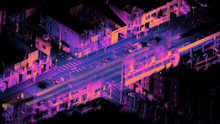
Ouster's OS1 lidar sensors provide the Postmates 'Serve' Autonomous Delivery Rover with the ability to sense, classify, and understand its immediate environment.[17][18][19]
In 2019 Ouster was selected by autonomous trucking startup Ike as a primary Lidar supplier to bring automated trucking to market.[20] It is also working with Coast Autonomous as Coast begins to ramp up production of self-driving passenger shuttles and autonomous utility vehicles.[21]
From 2019 Ouster has also been working with NVIDIA and Volvo Trucks to develop a scalable self-driving system for commercial use.[22]
In 2020 Ouster partnered with Chinese robotics company iDriverplus to provide lidar sensors for autonomous cleaning robots. After China entered into a state of emergency due to COVID-19, the two companies partnered to outfit a fleet of robots with OS1-64 lidar sensors. The unmanned cleaning and disinfection vehicles were equipped with OS1-64 lidar sensors on the top and front of the robots providing 360° 3D environmental monitoring and more accurate obstacle recognition.[23]
Models
| Name | OS0 | OS1 | OS2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Gen 2[24] | Gen 2[24] | Gen 2[24] |
| Announced | January 2020 | January 2020 | January 2020 |
| Channels | 32, 64, or 128 | 32, 64, or 128 | 32, 64, or 128 |
| Range | 55 m | 120 m | 240 m |
| Minimum Range | 0 m | 0 m | 0 m |
| Precision | ±1.5 – 5 cm | ±1.5 – 5 cm | ±1.5 – 5 cm |
| Field of View (Vertical) | 90° | 45° | 22.5° |
| Angular Resolution (Vertical) | 0.7° | 0.35° | 0.18° |
| Field of View (Horizontal) | 360º | 360º | 360º |
| Angular Resolution (Horizontal) | 512, 1024, or 2048 | 512, 1024, or 2048 | 512, 1024, or 2048 |
| Rotation Rate | 10 or 20 Hz | 10 or 20 Hz | 10 or 20 Hz |
| Data Points Per Second | 2,621,440 | 2,621,440 | 2,621,440 |
| Power Consumption | 14 – 20 W | 14 – 20 W | 18 - 24 W |
| Operating Voltage | 24 V nominal | 24 V nominal | 24 V nominal |
| Weight | 445 g | 455 g | 930 g |
| Diameter | 85 mm | 85 mm | 119.6 mm |
| Height (with cap) | 73.5 mm | 73.5 mm | 98.5 mm |
Awards and recognition
- In 2020, Ouster was an Honoree at the CES Innovation Awards for the OS2-128 LiDAR sensor within the Vehicle Intelligence & Transportation category.[25][26]
References
- "Ouster's Management". Ouster. Archived from the original on June 27, 2020. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- Korosec, Kirsten. "Postmates' self-driving delivery rover will see with Ouster's lidar". Autonomous Vehicle Engineering. Archived from the original on July 24, 2019. Retrieved October 6, 2018.
- "Ouster Profile". Crunchbase. Archived from the original on July 16, 2020. Retrieved July 15, 2020.
- Deutscher, Maria (January 3, 2019). "With new 128-laser sensor, Ouster ups the ante on LiDAR" (Emerging Tech). Silicon Angle. Archived from the original on July 18, 2020. Retrieved July 15, 2020.
- Anyadike, Nnamdi (November 3, 2019). "New LiDAR Technologies Boosting Autonomous Driving". Electro Pages. Archived from the original on July 16, 2020. Retrieved July 15, 2020.
- "Ouster Lidar Powers Next Generation Security and Safety Solutions". Associated Press. November 21, 2019. Archived from the original on July 16, 2020. Retrieved July 15, 2020.
- "Ouster introduces OS-1 128 Channel LiDAR Sensor". TAAS Magazine. January 3, 2019. Retrieved June 23, 2020.
- Lu, Daniel. "Lidar Mapping with Ouster 3D Sensors". Medium. Archived from the original on December 5, 2019. Retrieved July 15, 2020.
- Crichton, Danny (December 11, 2017). "LiDAR autonomous sensor startup Ouster announces $27M Series A led by auto powerhouse Cox Enterprises". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on July 17, 2020. Retrieved July 14, 2020.
- Wiggers, Kyle (March 25, 2019). "Ouster raises $60 million to ramp up lidar production" (Entrepreneur). VentureBeat. Archived from the original on July 16, 2020. Retrieved July 13, 2020.
- Korosec, Kirsten (March 25, 2019). "Lidar startup Ouster raises $60 million in production run-up". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on July 16, 2020. Retrieved July 15, 2020.
- Crichton, Danny (December 11, 2017). "LiDAR autonomous sensor startup Ouster announces $27M Series A led by auto powerhouse Cox Enterprises". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on July 17, 2020. Retrieved July 15, 2020.
- Yoshida, Junko (July 14, 2020). "Ouster Takes on Waymo with Lidar Diversity" (Automotive). EE Times. Archived from the original on July 15, 2020. Retrieved July 15, 2020.
- "OS2-128 Long-range lidar sensor". CES Technology Association. Archived from the original on July 17, 2020. Retrieved July 11, 2020.
- Chen, Yining (November 18, 2019). "Global LiDAR Companies and Their Latest Progresses in 2019: Mechanical LiDAR Suppliers". Trend Force Corp. LED Inside. Archived from the original on July 16, 2020. Retrieved July 15, 2020.
- The Robot Report Staff (November 17, 2019). "Ouster releases OS1-32 high-resolution, 32-channel lidar sensor". The Robot Report. Archived from the original on July 17, 2020. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- Williams, Andrew (July 6, 2020). "Lidar Technology in Autonomous Robotic Systems". Novus Light. Archived from the original on July 18, 2020. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- Korosec, Kirsten (July 24, 2019). "Postmates' self-driving delivery rover will see with Ouster's lidar". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on July 16, 2020. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- Ohnsman, Alan (July 24, 2019). "New Laser Eyes For Postmates Delivery Robot, Courtesy Of Ouster" (Transportation). Forbes. Archived from the original on July 16, 2020. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- "Ouster OS1 lidar sensor an integral component of Ike commercial trucking platform". LiDAR News. November 5, 2019. Archived from the original on July 16, 2020. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- Trego, Linda (July 29, 2019). "Ouster LiDAR speced in two AVs". Autonomous Vehicle Technology. Archived from the original on July 18, 2020. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- Yvkoff, Liane (September 18, 2019). "Using Ouster's Lidar, Nvidia Targets 2022 For Commercial Launch Of Self-Driving Vehicles" (Transportation). Forbes. Archived from the original on July 17, 2020. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- Muir, James (May 14, 2020). "Ouster provides iDriverplus with lidar". Autonomous Vehicle International. Archived from the original on July 16, 2020. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- "Explore and compare different Ouster digital lidar sensors". Ouster. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- Cuneo, Elizabeth (January 6, 2020). "Ouster releases two high-resolution digital LiDAR sensors" (CES 2020). Autonomous Vehicle Technology. Archived from the original on July 16, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2020.
- "OS2-128 Long-range lidar sensor". CES Technology Association. Archived from the original on July 17, 2020. Retrieved July 15, 2020.