Orthophoto
An orthophoto, orthophotograph or orthoimage is an aerial photograph or satellite imagery geometrically corrected ("orthorectified") such that the scale is uniform: the photo or image follows a given map projection. Unlike an uncorrected aerial photograph, an orthophoto can be used to measure true distances, because it is an accurate representation of the Earth's surface, having been adjusted for topographic relief,[1] lens distortion, and camera tilt.
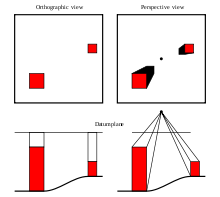


Orthophotographs are commonly used in geographic information systems (GIS) as a "map accurate" background image. An orthorectified image differs from "rubber sheeted" rectifications as the latter may accurately locate a number of points on each image but "stretch" the area between so scale may not be uniform across the image. A digital elevation model (DEM) is required to create an accurate orthophoto as distortions in the image due to the varying distance between the camera/sensor and different points on the ground need to be corrected. An orthoimage and a "rubber sheeted" image can both be said to have been "georeferenced"; however, the overall accuracy of the rectification varies. Software can display the orthophoto and allow an operator to digitize or place linework, text annotations or geographic symbols (such as hospitals, schools, and fire stations). Some software can process the orthophoto and produce the linework automatically.
Production of orthophotos was historically achieved using mechanical devices.[2]
Orthophotomap
.jpg)
An orthophotomosaic is a raster image made by merging orthophotos — aerial or satellite photographs which have been transformed to correct for perspective so that they appear to have been taken from vertically above at an infinite distance.[3] Google Earth images are of this type.
The document (digital or paper) representing an orthophotomosaic with additional marginal information like a title, north arrow, scale bar and cartographical information is called an orthophotomap or image map. Often these maps show additional point, line or polygon layers (like a traditional map) on top of the orthophotomosaic. A similar document, mostly used for disaster relief, is called a spatiomap.
See also
- Aerial Photography
- Digital Orthophoto Quadrangle (DOQ) and Digital Orthophoto Quarter Quadrangle (DOQQ)
- Leica Photogrammetry Suite Orthorectification Software
- GRASS GIS (i.ortho.photo module)
- Photogrammetry
- Photomapping
- TopoFlight
- Socet set Orthophoto Software
- U.S. Geological Survey
- Rational Polynomial Coefficient
References
- Smith, Gary S. "DIGITAL ORTHOPHOTOGRAPHY AND GIS." ESRI Conference. http://proceedings.esri.com/library/userconf/proc95/to150/p124.html
- BBC Tomorrow's World: How maps are corrected and updated using aerial photography and optical machinery. 18 December 1970.
- American Congress on Surveying and Mapping, American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (1994), Glossary of the Mapping Sciences, American Society of Civil Engineers, p. 370, ISBN 9780784475706
- Bolstad, P., (2005), GIS Fundamentals: A First Text on Geographic Information Systems, Eider Press, White Bear Lake, MN, 2nd ed.
- Demers, Michael N., (1997). Fundamentals of Geographic Information Systems, John Wiley & Sons.
- Fernandez, E., Garfinkel, R. & Roman Arbiol (May–June 1998). "Mosaicking of Aerial Photographic Maps Via Seams Defined by Bottleneck Shortest Paths". Operations Research. 46 (3): 293–304. doi:10.1287/opre.46.3.293.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link).
- Petrie, G., (1977), Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers: Orthophotomaps New Series, vol. 2, no.1, Contemporary Cartography., pg. 49-70
- Robinson, A.H., Morrison, J.L., Muehrcke, P.C., Kimerling, A.J., Stephen Guptill, (1995) Elements of Cartography: John Wiley & Sons Inc., Canada, 6th ed.
- United States Geological Survey, US Department of Interior, USGS Fact Sheet May 2001 http://erg.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/factsheets/fs05701.html
