OpenPuff
OpenPuff Steganography and Watermarking, sometimes abbreviated OpenPuff or Puff, is a free steganography tool for Microsoft Windows created by Cosimo Oliboni and still maintained as independent software. The program is notable for being the first steganography tool (version 1.01 released on December 2004) that:
- lets users hide data in more than a single carrier file. When hidden data are split among a set of carrier files you get a carrier chain, with no enforced hidden data theoretical size limit (256MB, 512MB, ... depending only on the implementation)
- implements 3 layers of hidden data obfuscation (cryptography, whitening and encoding)
- extends deniable cryptography into deniable steganography
 OpenPuff v4.00 screenshot | |
| Developer(s) | Eng. Cosimo Oliboni |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 4.01
/ July 19, 2018 |
| Operating system | Windows |
| Type | Steganography tool |
| License | LGPL (Free Software) |
| Website | HomePage |
Last revision supports a wide range of carrier formats
Use
OpenPuff is used primarily for anonymous asynchronous data sharing:
- the sender hides a hidden stream inside some public available carrier files (password + carrier files + carrier order are the secret key)
- the receiver unhides the hidden stream knowing the secret key
The advantage of steganography, over cryptography alone, is that messages do not attract attention to themselves. Plainly visible encrypted messages — no matter how unbreakable — will arouse suspicion, and may in themselves be incriminating in countries where encryption is illegal. Therefore, whereas cryptography protects the contents of a message, steganography can be said to protect both messages and communicating parties.
Watermarking is the action of signing a file with an ID or copyright mark. OpenPuff does it in an invisible steganographic way, applied to any supported carrier. The invisible mark, being not password protected, is accessible by everyone (using the program).[1]
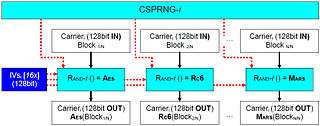
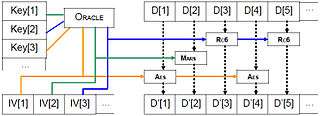
Multi-cryptography
OpenPuff is a semi-open source program:
- cryptography, CSPRNG, hashing (used in password hexadecimal extension), and scrambling are open source
Cryptographic algorithms (16 taken from AES, NESSIE and CRYPTREC) are joined into a unique multi-cryptography algorithm:
- keys and internal static data are initialized for each algorithm f
- each data block D [ i ] (128bit) will be encrypted using a different algorithm f [ i ]
- f [ i ] is chosen with a pseudorandom oracle, seeded with a second independent password[2]
1. Choosing the cryptography algorithm for data block i f [ i ] = rand ( Oracle )
2. Applying cryptography to data block i Cipher ( D [ i ] ) = f [ i ] ( D [ i ] )
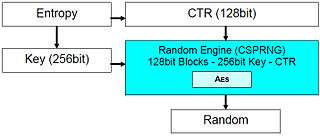
Statistical resistance
Extensive testing has been performed on the statistical resistance properties of the CSPRNG and multi-cryptography modules, using the ENT,[3] NIST [4] and DIEHARD test suites. Provided results are taken from 64KB, 128KB, ... 256MB samples:
- bit entropy test: >7.9999xx / 8.000000
- compression test: 0% size reduction after compression
- chi square distribution test: 40% < deviation < 60%
- mean value test: 127.4x / 127.5
- Monte Carlo test: error < 0.01%
- serial correlation test: < 0.0001
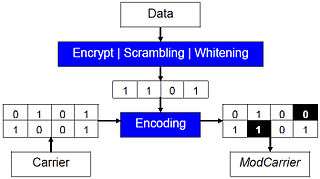
Steganalysis resistance
Security, performance and steganalysis resistance are conflicting trade-offs.[5]
[Security vs. Performance]: Whitening
- Pro: ensures higher data security
- Pro: allows deniable steganography
- Con1: requires a lot of extra carrier bits
[Security vs. Steganalysis]: Cryptography + Whitening
- Pro: ensure higher data security
- Con2: their random statistical response marks carriers as more "suspicious"
Data, before carrier injection, is encrypted and whitened: a small amount of hidden data turns into a big chunk of pseudorandom "suspicious data". Carrier injection encodes it using a non linear covering function[6] that takes also original carrier bits as input. Modified carriers will need much less change (Con1) and, lowering their random-like statistical response, deceive many steganalysis tests (Con2).
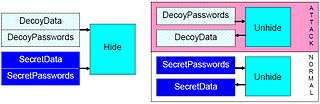
Deniable steganography
There will always be a non-negligible probability of being detected, even if the hidden stream behaves like a “natural container” (unpredictable side-effects, being caught in Flagrante delicto, etc.). Resisting these unpredictable attacks is also possible, even when the user is forced (by legal or physical coercion) to provide a valid password.[7][8] Deniable steganography (a decoy-based technique) allows the user to deny convincingly the fact that sensitive data is being hidden. The user needs to provide some expendable decoy data that he would plausibly want to keep confidential and reveal it to the attacker, claiming that this is all there is.
References
- Sécurité des réseaux : Stéganographie et tatouage numérique
- OpenPuff Manual
- ENT - A Pseudorandom Number Sequence Test Program
- NIST - A Statistical Test Suite for the Validation of Random Number Generators and Pseudo Random Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications
- Provos, Niels. "Defending against statistical steganalysis". Proceedings of the 10th Conference on USENIX Security Symposium. SSYM'01. 10: 24–37. Retrieved 28 November 2012.
- Bierbrauer, Jürgen; Fridrich, Jessica (2008). Constructing good covering codes for applications in Steganography. Transactions on Data Hiding and Multimedia Security III. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 4920. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. pp. 1–22. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.72.5242. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-69019-1_1. ISBN 978-3-540-69019-1. Retrieved 19 July 2018.
- Sergienko, Greg S. "Self Incrimination and Cryptographic Keys". Richmond Journal of Law and Technology. 2 (1). Retrieved 19 July 2018.
- Julian Assange - Physical Coercion