Onega Peninsula
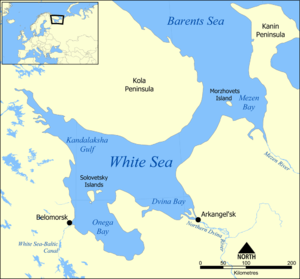
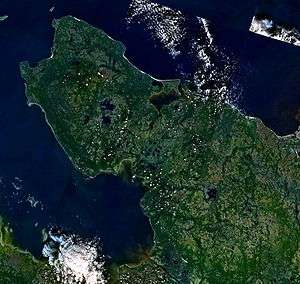
The Onega Peninsula is located in Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It protrudes into the White Sea, with Onega Bay to the south-west, and Dvina Bay to the north-east. The length of the peninsula is about 150 kilometres (93 mi), and the width varies between 60 kilometres (37 mi) and 75 kilometres (47 mi).[1]
Geography
The coastal area of the peninsula is populated. The villages (counterclockwise) of Nyonoksa, Syuzma, Krasnaya Gora, Pertominsk, Unsky, Yarenga, Lopshenga, Letny Navolok, Letnyaya Zolotitsa, Pushlakhta, Lyamtsa, Purnema, and Nizhmozero are all located at or near the coast. The north-eastern coast of the peninsula is crossed by the Una Bay, a gulf in the Dvina Bay, which is about 20 kilometres (12 mi) long. The villages of Una and Luda are located at the inner coast of the Una Bay. The interior of the peninsula (north-west of the line connecting Luda and Purnema) is a wilderness without any permanent population. There is some logging at Verkhneozersk, south-east of Luda. The interior of the peninsula is hilly, and there are many lakes, the biggest of which are Lake Myandozero, Lake Vezhmozero (both lakes drain to the Vezhma River - a tributary of the Una Bay), Lake Lyamitskoye (which drains to the Lyamtsa River, flowing west), and Lake Bolshoye Vygozero (which drains into the Zolotitsa River, also flowing west).
Administration
Administratively, the peninsula is shared between Onezhsky and Primorsky Districts and the city of Severodvinsk of Arkhangelsk Oblast. On 17 December 1940 Belomorsky District was established on the peninsula, on the areas which previously were parts of Primorsky and Onezhsky Districts. The administrative center of the district became the selo of Pertominsk. On 30 September 1958 Belomorsky District was abolished, and the area of the district was shared between Primorsky and Onezhsky Districts.[2]
History and religion
The peninsula was settled by Novgorodians not later than the 13th century. The Pomors, living at the coast, are the descendants of the Novgorodians. Most of the villages on the coast of the peninsula have a historical significance. The ensemble of the Purnema Pogost, consisting of St. Nicholas' Church (1618) and the Nativity Church (1860), and the Zaostrovsky Pogost in the village of Nyonoksa, consisting of the Church of the Presentation of Jesus in the Temple (1683-1688) and the St. Michael Church (1776-1785), are protected at the federal level as a monument of architecture.[3]
The village of Lopshenga was featured in the works of Yury Kazakov, a Russian short story writer who traveled extensively in the Russian North. The name of one of the Kazakov's books of short stories is Poedemte v Lopshengu — Let us go to Lopshenga.
Economy and transportation
The economy of the peninsula is based on the timber production and fishery. The village of Luda is connected by an all-season road to Severodvinsk and Onega. There is a boat ferry across the Una Bay. Other villages at the coast have infrequent air and sea connections to Onega and Arkhangelsk.
A national park, Onezhskoye Pomorye National Park, was opened on the coast of the Onega Peninsula in 2013 to protect pristine forests.[4]
References
- Онежский полуостров // Север (in Russian). Moscow: Физкультура и спорт. 1975.
- "АДМИНИСТРАТИВНО-ТЕРРИТОРИАЛЬНОЕ ДЕЛЕНИЕ АРХАНГЕЛЬСКОЙ ГУБЕРНИИ В XVIII-XX вв. * (СПРАВКА)" (in Russian). Архивы России. 2000. Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2011.
- Памятники истории и культуры народов Российской Федерации (in Russian). Russian Ministry of Culture. Archived from the original on 16 April 2009. Retrieved 22 August 2011.
- "Создан новый национальный парк «Онежское Поморье»" (in Russian). Greenpeace. 27 February 2013. Retrieved 2 November 2015.