Ohio State Route 338
State Route 338 (SR 338) was a state highway in the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Ohio, entirely in Meigs County. Running along the Ohio River, the route existed from 1932 until about 2012. For most of its history, SR 338 ran along the river between Racine and Lebanon Township with both ends at SR 124. At the time of its removal from the state highway system, the last remnant of the route was a 2.3-mile-long (3.7 km) segment (designated by the Ohio Department of Transportation (ODOT) as SR 338-J) between US 33 near the Ravenswood Bridge and SR 124.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
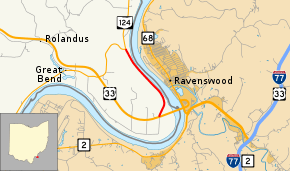 Route of SR 338-J (c. 2008) highlighted in red | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Maintained by ODOT | ||||
| Length | 2.32 mi[1] (3.73 km) | |||
| Existed | 1932–by 2012 | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| West end | ||||
| East end | ||||
| Location | ||||
| Counties | Meigs | |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
Route description
.svg.png)
The following description is the description of SR 338-J c. 2008
SR 338 began at an intersection with US 33 near Racine. The route headed northward, running near the banks of the Ohio River. SR 338 intersected with a few private roads leading to nearby homes. A field is visible to the east, as the highway made its namesake turn as Great Bend Road. Through the bend, SR 338 turned and headed into a dense forest. After a short distance, SR 338 broke out of the dense patch of trees. With the Ohio River in view, the highway terminated at an intersection with SR 124 northeast of Racine.[2]
History
The original route was certified in 1932; originally routed from Letart Falls (about 6 miles (9.7 km) south of Racine) to 10 miles (16 km) east of Letart Falls.[3][4] The highway was extended to Racine in 1937 along a previously unnumbered road from Letart Falls to Antiquity, and along the former SR 337 from Antiquity to Racine.[5][6] SR 338 was extended 8.5 miles (13.7 km) east of Racine along the previous and current alignment of SR 124.[7]
In 1941, SR 338 swapped alignments with SR 124 from 6.5 miles (10.5 km) to 8.5 miles (13.7 km) east of Racine; SR 338 was given the southern alignment along the Ohio River.[8] By 2003, SR 338 was truncated at the new alignment of US 33 approximately 10 miles (16 km) east of Racine; the former alignment of SR 338 from Racine south along the river and back up north to 6.25 miles (10.06 km) east of Racine designated as SR 124; from 6.75 miles (10.86 km) east of Racine to US 33 decertified.[9][10]
When SR 338 was truncated in 2003, the remains of the highway became known as SR 338-J.[1] At the time of the truncation, the route was unsigned and the "J" suffix meant that the route was awaiting abandonment.[11] ODOT was making constant repairs to SR 338 due to its close proximity to the river, which led to soil instability.[12] Between 2008 and 2012, the last segment of SR 338 had been removed from the state's jurisdiction.[13][14] Part of the road itself had been abandoned leaving the former SR 338 as two separate township-maintained roads at either end.[14] Today, the former SR 338 is designated SR 124 between Racine and the intersection of SR 124 and Great Bend Road, Meigs County Road 338-A along Great Bend Road between SR 124 and US 33, Stone Road (Township Road 708) between US 33 and a dead end, and Cleek Road (Township Road 707) between a dead end and SR 124 near Portland.[14][15]
Major intersections
1941–2003 route
The entire route was in Meigs County.
| Location | mi[16] | km | Destinations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Racine | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||
| Lebanon Township | 15.55 | 25.03 | Western end of SR 124 concurrency | ||
| 16.01 | 25.77 | Eastern end of SR 124 concurrency | |||
| 19.46 | 31.32 | Western terminus of SR 824; later US 33T and US 33 | |||
| 21.72 | 34.95 | ||||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| |||||
2003–2012 route
The entire route was in Lebanon Township, Meigs County.
| mi[1] | km | Destinations | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| 2.32 | 3.73 | ||||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
References
- Ohio Department of Transportation. "Technical Services Straight Line Diagrams - SR 338-J" (PDF). Retrieved July 6, 2013.
- Google (November 1, 2015). "overview map of SR 338 (2008)" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved November 1, 2015.
- Ohio Highway map (Map). Ohio Department of Transportation. 1931.
- Ohio Highway map (Map). Ohio Department of Transportation. 1932.
- Ohio Highway map (Map). Ohio Department of Transportation. 1936.
- Ohio Highway map (Map). Ohio Department of Transportation. 1937.
- Ohio Highway map (Map). Ohio Department of Transportation. 1938.
- Ohio Highway map (Map). Ohio Department of Transportation. 1941.
- Official Transportation Map of Ohio (Map). Ohio Department of Transportation. 2003.
- Official Transportation Map of Ohio (Map). Ohio Department of Transportation. 2007.
- "Legend for Straight Line Diagrams" (PDF). ODOT. p. 2. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- "Inclinometer – Time Domain Reflectometry Comparative Study" (PDF). Russ College of Engineering and Technology, Ohio University for ODOT. December 2004. p. 17. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- "ROADWAY DESCRIPTION INVENTORY REPORT - DESTAPE". ODOT. May 13, 2008. Archived from the original on January 1, 2009. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- Meigs County (PDF) (Map). ODOT. June 2012. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- "OHIO DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION - OFFICE OF TECHNICAL SERVICES ROAD INVENTORY SYSTEM RI-134A LISTING OF LOCAL ROADS INVENTORY SECTIONS (Meigs County)" (PDF). ODOT. May 14, 2013. pp. 13, 75. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- "2001 MEIGS CO 2 AVERAGE 24-HR TRAFFIC VOLUME" (PDF). ODOT. 2001. pp. 2–3. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
