Halver
Halver is a town in the Märkischer Kreis district, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It has a population of 18,083 (2004) and covers an area of 77.37 km², of which 51% are used for agricultural purposes and 35% are forest. It is located in the hills of the Sauerland; at its highest elevation it is 440 m above sea level.
Halver | |
|---|---|
 Halver town hall in 2008 | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Halver within Märkischer Kreis district 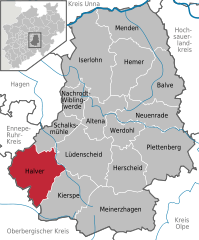  | |
 Halver  Halver | |
| Coordinates: 51°11′N 07°28′E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia |
| Admin. region | Arnsberg |
| District | Märkischer Kreis |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Michael Brosch (SPD) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 77.37 km2 (29.87 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 440 m (1,440 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 16,106 |
| • Density | 210/km2 (540/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 58553 |
| Dialling codes | 02353 |
| Vehicle registration | MK |
| Website | www.halver.de |
History
Around 950 the Oberhof Halvara was first mentioned in the Werdener Probsteiregister. For more than 500 years Halver was the seat of a Fehmic court, the earliest definite evidence of which is in 1243; it ceased to exist in 1753. This court was most famous because of the trial of duke Henry XVI the Rich of Bavaria-Landshut and the knight of Toerring on May 2, 1430.
With effect from October 1, 1912 the municipality Halver was split, Schalksmühle becoming an independent municipality. Both were administered together in the Amt Halver. As part of the communal reforms of the district of Altena the Amt was dissolved on January 1, 1969, and Halver was granted city rights.



Coat of arms
The red and white checked base refers to the fess from the arms of the Counts of the Mark. The stone judgement table under a linden tree represents the Feme court. It was designed by Otto Hupp, and was granted on March 29, 1935.
The Amt Halver had a separate coat of arms, which was also designed by Otto Hupp. It combined elements from the two member municipalities Halver and Schalksmühle: in the upper part is a linden branch symbolizing Halver, in the bottom the upper half of a black mill wheel as the symbol of Schalksmühle. Separating the two is the red and white checked fess, as above. The coat of arms was granted on June 8, 1936, and expired with the dissolving of the Amt in 1969.
Districts
Additionally to the core city, there are the following districts, many of them are very small. Ahe | Altemühle | Anschlag | Auf dem Heede | Auf dem Wiebusch | Auf den Eicken | Auf den Kuhlen | Auf der Bever | Auf der Brake | Auf der Mark | Bärendahl | Beisen | Beiserohl | Becke | Berge | Bergfeld | Berken | Birkenbaum | Bochen | Bocherplatz | Bommert | Borkshof | Brenscheid | Brocksiepen | Bruch | Brüninghausen | Büchen | Büchenbaum | Büchermühle | Burbach | Burg | Buschhauser Hammer | Carthausen | Collenberg | Clev | Dahlhausen | Dicksiepen | Diekerhof | Dommelnheide | Dornbach | Dörnen | Edelkirchen | Ehberg | Ehringhausen | Eichhofermühle | Eichholz | Eickerhöhe | Eickerschmitte | Engstfeld | Eschen | Eversberge | Gehärte | Gesenberg | Giersiepen | Glörfeld | Grafweg | Grund | Grünenbaum | Grünewald | Hagebüchen | Hagebücherhöh | Hagedorn | Hakenberg | Halloh | Halverscheid | Handweiser | Hartmecke | Heerenfelde | Heesfeld | Heesfelder Hammer | Heesfelder Mühle | Hefendehl | Heinken-Hedfeld | Herweger Schleifkotten | Hesseln | Hinterhedfeld | Hohenplanken | Hohl | Holte | Howarde | Hulvershorn | Husen | Im Heede | Im Sumpf | Im Wiebusch | In den Eicken | In der Hälver | Kamscheid | Kirchlöh | Kotten | Krause Buche | Kreimendahl | Kreisch | Kreuzweg | Kückelhausen | Landwehr | Lausberge | Lingen | Lingensiepen | Löhbach | Löhrmühle | Lömmelscheid | Magdheide | Mesenhohl | Mittelcarthausen | Mittelherweg | Niederbolsenbach | Niederbommert | Niederbuschhausen | Niederennepe | Niederhedfeld | Niederhövel | Niederhürxtal | Niederlangenscheid | Niedervahlefeld | Neuenhaus | Neuenherweg | Neuenvahlefeld | Nonnenennepe | Nordeler Schleifkotten | Nordeln | Oberbolsenbach | Oberbommert | Oberbrügge | Oberbuschhausen | Obercarthausen | Oberherweg | Oberhövel | Oberhürxtal | Oberlangenscheid | Obervahlefeld | Oeckinghausen | Oege | Oesterberg | Osenberg | Ostendorf | Othmaringhausen | Pottheinrich | Rothenbruch | Schanzmannsmühle | Schlachtenrade | Schlade | Schlechtenbach | Schlemme | Schmalenbach | Schmidthausen | Schmidtsiepen | Schneehohl | Schöneberge | Schröders Herweg | Schüreichhofen | Schulten Hedfeld | Schwenke | Siepen | Solberg | Sondern | Steinbach | Stenkenberg | Sticht | Stichterweide | Stieneichhofen | Stöcken | Streitstück | Sundern | Vahlefelderheide | Vömmelbach | Vormbaum | Vorst | Voswinkel | Walde | Wegerhof | Weißenpferd | Wiebusch-Hedfeld | Wiene | Wilhelmshöh | Winkhof | Wöste (They all have an own article in dewiki)
Number of inhabitants
Municipality Halver
- 1915: 6.476
- 1925: 7.729
- 1935: 8.122
- 1939: 8.772
- 1946: 12.045
- 1961: 13.684
- 1968: 15.713
Town Halver
- 1969: 16.254
- 1978: 16.176
- 1988: 15.399
- 1995: 16.983
- 1999: 17.876
- 2003: 18.111
- 2006: 17.776
- 2008: 17.465
- 2010: 17.159
- 2012: 16.300
- 2014: 16.677[2]
Mayor
At the election in 2015, Michael Brosch (SPD) became the new mayor in Halver, he won against his predecessor Dr. Bernd Eicker.
International relations
The town twinning with the Swedish city Katrineholm originated from the connection between a music group from Halver and a traditional dancing group from Katrineholm. It was officially signed on September 30, 1963.
On April 25, 1975 the twinning agreement with the French city Hautmont was signed. There has also been a city friendship with Pardess-Hanna in Israel since 1989.
Sons and daughters of the town
- Eugen Schmalenbach (1873-1955), economist, the local commercial vocational school was named after him
References
- "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden Nordrhein-Westfalens am 31. Dezember 2018" (in German). Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- "Zahlen & Statistik". halver.de (in German). Retrieved 2015-12-07.