Overall equipment effectiveness
Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) is a measure of how well a manufacturing operation is utilized (facilities, time and material) compared to its full potential, during the periods when it is scheduled to run. It identifies the percentage of manufacturing time that is truly productive. An OEE of 100% means that only good parts are produced (100% quality), at the maximum speed (100% performance), and without interruption (100% availability).
Measuring OEE is a manufacturing best practice. By measuring OEE and the underlying losses, important insights can be gained on how to systematically improve the manufacturing process. OEE is an effective metric for identifying losses, bench-marking progress, and improving the productivity of manufacturing equipment (i.e., eliminating waste)
Total effective equipment performance (TEEP) is a closely related measure which quantifies OEE against calendar hours rather than only against scheduled operating hours. A TEEP of 100% means that the operations have run with an OEE of 100% 24 hours a day and 365 days a year (100% loading).
The term OEE was coined by Seiichi Nakajima.[1] It is based on the Harrington Emerson way of thinking regarding labor efficiency. The generic form of OEE allows comparison between manufacturing units in differing industries. It is not however an absolute measure and is best used to identify scope for process performance improvement, and how to get the improvement.[2] OEE measurement is also commonly used as a key performance indicator (KPI) in conjunction with lean manufacturing efforts to provide an indicator of success. OEE can be illustrated by a brief discussion of the six metrics that comprise the system (the "Six Big Losses").
Calculations for OEE and TEEP
The OEE of a manufacturing unit are calculated as the product of three separate components:
- Availability: percentage of scheduled time that the operation is available to operate. Often referred to as Uptime.
- Performance: speed at which the Work Center runs as a percentage of its designed speed.
- Quality: Good Units produced as a percentage of the Total Units Started. It is commonly referred to as the first pass yield (FPY).
To calculate the TEEP, the OEE is multiplied by a fourth component:
- Loading: percentage of total calendar time that is actually scheduled for operation.
The calculations of OEE are not particularly complicated, but care must be taken as to standards that are used as the basis. Additionally, these calculations are valid at the work center or part number level but become more complicated if rolling down to aggregate levels.[3]
Overall equipment effectiveness
Each of the three components of the OEE points to an aspect of the process that can be targeted for improvement. OEE may be applied to any individual Work Center, or rolled up to Department or Plant levels. This tool also allows for drilling down for very specific analysis, such as a particular Part Number, Shift, or any of several other parameters. It is unlikely that any manufacturing process can run at 100% OEE. Many manufacturers benchmark their industry to set a challenging target; 85% is not uncommon.
- OEE is calculated with the formula (Availability)*(Performance)*(Quality)
- Using the examples given below:
- (Availability= 86.6%)*(Performance=93%)*(Quality=91.3%)= (OEE=73.6%)
Alternatively, and often easier, OEE is calculated by dividing the minimum time needed to produce the parts under optimal conditions by the actual time needed to produce the parts. For example:
- Total Time: 8 hour shift or 28,800 seconds, producing 14,400 parts, or one part every 2 seconds.
- Fastest possible cycle time is 1.5 seconds, hence only 21,600 seconds would have been needed to produce the 14,400 parts. The remaining 7,200 seconds or 2 hours were lost.
- The OEE is now the 21,600 seconds divided by 28,800 seconds (same as minimal 1.5 seconds per part divided by 2 actual seconds per part), or 75%.
Total effective equipment performance
Whereas OEE measures effectiveness based on scheduled hours, TEEP measures effectiveness against calendar hours, i.e.: 24 hours per day, 365 days per year.
TEEP, therefore, reports the 'bottom line' utilization of assets.
TEEP = Loading * OEE[3]
Loading
The Loading portion of the TEEP Metric represents the percentage of time that an operation is scheduled to operate compared to the total Calendar Time that is available. The Loading Metric is a pure measurement of Schedule Effectiveness and is designed to exclude the effects how well that operation may perform.
Calculation: Loading = Scheduled Time / Calendar Time
Example:
A given Work Center is scheduled to run 5 Days per Week, 24 Hours per Day.
For a given week, the Total Calendar Time is 7 Days at 24 Hours.
Loading = (5 days x 24 hours) / (7 days x 24 hours) = 71.4%
Availability
The Availability portion of the OEE Metric represents the percentage of scheduled time that the operation is available to operate. The Availability Metric is a pure measurement of Uptime that is designed to exclude the effects of Quality and Performance. The losses due to wasted availability are called availability losses.[4]
Example: A given Work Center is scheduled to run for an 8-hour (480 minute) shift with a 30-minute scheduled break and during the break the lines stop, and unscheduled downtime is 60 minutes.
The scheduled time = 480 minutes - 30 minutes = 450 minutes.
Operating Time = 480 Minutes – 30 Minutes Schedule Loss – 60 Minutes Unscheduled Downtime = 390 Minutes
Calculation: Availability = operating time / scheduled time[5]
Availability = 390 minutes / 450 minutes = 86.6%
Performance and productivity
Also known as "process rate", the Performance portion of the OEE Metric represents the speed at which the Work Center runs as a percentage of its designed speed. The Performance Metric is a pure measurement of speed that is designed to exclude the effects of Quality and Availability. The losses due to wasted performance are also often called speed losses. In practice it is often difficult to determine speed losses, and a common approach is to merely assign the remaining unknown losses as speed losses.
Calculation: Performance (Productivity) = (Parts Produced * Ideal Cycle Time) / Operating time [6]
Example:
A given Work Center is scheduled to run for an 8-hour (480 minute) shift with a 30-minute scheduled break.
Operating Time = 450 Min Scheduled – 60 Min Unscheduled Downtime = 390 Minutes
The Standard Rate for the part being produced is 40 Units/Hour or 1.5 Minutes/Unit
The Work Center produces 242 Total Units during the shift. Note: The basis is Total Units, not Good Units. The Performance metric does not penalize for Quality.
Time to Produce Parts = 242 Units * 1.5 Minutes/Unit = 363 Minutes
Performance (Productivity) = 363 Minutes / 390 Minutes = 93.1%
Quality
The Quality portion of the OEE Metric represents the Good Units produced as a percentage of the Total Units Started. The Quality Metric is a pure measurement of Process Yield that is designed to exclude the effects of Availability and Performance. The losses due to defects and rework are called quality losses and quality stops. Reworked units which have been corrected are only measured as unscheduled downtime while units being scrapped can affect both operation time and unit count.
Calculation: Quality = (Units produced - defective units) / (Units produced)[5]
Example:
242 Units are produced. 21 are defective.
(242 units produced - 21 defective units) = 221 units
221 good units / 242 total units produced = 91.32%
"Six Big Losses"
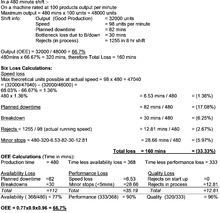
To be able to better determine the sources of the greatest loss and to target the areas that should be improved to increase performances, these categories (Availability, Performance and Quality) have been subdivided further into what is known as the ‘Six Big Losses’ to OEE.
These are categorized as follows:
| Availability | Performance | Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Planned Downtime | Minor Stops | Production Rejects |
| Breakdowns | Speed Loss | Rejects on Start up |
The reason for identifying the losses in these categories is so that specific countermeasures can be applied to reduce the loss and improve the overall OEE.
Total Productive Maintenance
Continuous improvement in OEE is the goal of TPM (Total Productive Maintenance). Specifically, the goal of TPM as set out by Seiichi Nakajima is "The continuous improvement of OEE by engaging all those that impact on it in small group activities". To achieve this, the TPM toolbox sets out a Focused improvement tactic to reduce each of the six types of OEE loss. For example the Focused improvement tactic to systematically reduce breakdown risk sets out how to improve asset condition and standardise working methods to reduce human error and accelerated wear.
Combining OEE with Focused improvement converts OEE from a lagging to a leading indicator. The first Focused improvement stage of OEE improvement is to achieve a stable OEE. One which varies at around 5% from the mean for a representative production sample. Once an asset effectiveness is stable and not impacted by variability in equipment wear rates and working methods. The second stage of OEE improvement (optimisation) can be carried out to remove chronic losses. Combining OEE and TPM Focused improvement tactics creates a leading indicator that can be used to guide performance management priorities. As the TPM process delivers these gains through small cross functional improvement teams, the process of OEE improvement raises front line team engagement/problem ownership, collaboration and skill levels. It is this combination of OEE as a KPI, TPM Focused improvement tactics and front line team engagement that locks in the gains and delivers the TPM goal of year on year improvement in OEE.
Heuristic
OEE is useful as a heuristic, but can break down in several circumstances. For example, it may be far more costly to run a facility at certain times. Performance and quality may not be independent of each other or of availability and loading. Experience may develop over time. Since the performance of shop floor managers is at least sometimes compared to the OEE, these numbers are often not reliable, and there are numerous ways to fudge these numbers.[7]
OEE has properties of a geometric mean. As such it punishes variability among its subcomponents. For example, 20% * 80% = 16%, whereas 50% * 50% = 25%. When there are asymmetric costs associated with one or more of the components, then the model may become less appropriate.
Consider a system where the cost of error is exceptionally high. In such a condition, higher quality may be far more important in a proper evaluation of effectiveness than performance or availability. OEE also to some extent assumes a closed system and a potentially static one. If one can bring in additional resources (or lease out unused resources to other projects or business units) then it may be more appropriate for example to use an expected net present value analysis.
Variability in flow can also introduce important costs and risks that may merit further modeling. Sensitivity analysis and measures of change may be helpful.
Further reading
- Hansen, Robert C (2005). Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). Industrial Press. ISBN 978-0-8311-3237-8.
- Koch, Arno (2007). OEE for the Production Team. Makigami. ISBN 978-90-78210-08-5. (English). ISBN 978-90-78210-07-8 (Dutch)., ISBN 978-3-940775-04-7 (German).
- Productivity Press Development Team (1999), OEE for Operators: Overall Equipment Effectiveness, Productivity Press, ISBN 978-1-56327-221-9
- OEE and derived indicators TEEP, PEE, OAE, OPE, OFE, OTE and CTE, MES Center Association
See also
References
- "Origin of OEE". OEE Foundation. Retrieved 15 July 2015.
- "Understanding OEE". Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- "OEE Overview - with Calculation Methods" (PDF). Retrieved 23 September 2013.
- "Understanding Availability". Retrieved 9 October 2014.
- "Calculate OEE - Simple Calculator & OEE Formulas". SensrTrx | Cloud Manufacturing Analytics. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- "OEE Primer: Calculating OEE". Retrieved 9 July 2013.
- "Top Three Methods on how to Fudge Your OEE". Retrieved 5 January 2014.