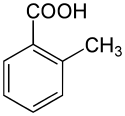
o-Toluic acid
o-Toluic acid, also 2-methylbenzoic acid, is an aromatic carboxylic acid, with formula (CH3)C6H4(COOH). It is an isomer of p-toluic acid and m-toluic acid. When purified and recrystallized, o-toluic acid forms needle-shaped crystals. o-Toluic acid was first noticed by Sir William Ramsay, credited discoverer of the noble gases and winner of the 1904 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylbenzoic acid | |||
| Other names
ortho-toluic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.896 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 136.2 g/mol | ||
| Density | 1.06 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 104 to 105 °C (219 to 221 °F; 377 to 378 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 259 °C (498 °F; 532 K) | ||
| -80.83·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
o-Toluic acid is prepared by oxidation of o-xylene with nitric acid.[2]
References
- O-TOLUIC ACID - Compound Summary, PubChem.
- Harold E. Zaugg, Richard T. Rapala (1947). "o-Toluic Acid". Org. Synth. 27: 84. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.027.0084.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.