Nitrotriazolone
Nitrotriazolone (NTO) is a high explosive developed in the weapons program, [2] first identified in 1905, but research into its explosive properties was not fully undertaken until the 1980s, [3] used by the US Army in munitions.[4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
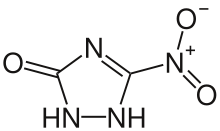
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-nitro-1,2-dihydro-1,2,4-triazol-3-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | NTO |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.050 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | C420648 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UN number | 0490 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H2N4O3 | |
| Molar mass | 130.063 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Nitrotriazolone is being progressively made use of in novel explosive formulations. [5]
References
- "Nitrotriazolone". PubChem. National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- High-performance Computing. The Laboratory. 1993.
- Jai Prakash Agrawal (20 November 2015). High Energy Materials: Propellants, Explosives and Pyrotechnics. Wiley. pp. 124–. ISBN 978-3-527-80268-5.
- Winstead, Bob (26 October 2011). "Nitrotriazolone: An Environmental Odyssey" (PDF). NDIA Systems Engineering Conference. Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- Shree Nath Singh (4 August 2013). Biological Remediation of Explosive Residues. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 285–. ISBN 978-3-319-01083-0.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.