New Copenhagen
New Copenhagen (Danish: Ny København) or St. Ann's Town (Danish: Sankt Annæ By) was a 17th-century expansion of fortified Copenhagen, Denmark.
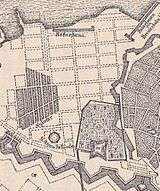
The original plan for the area, from 1649, was later abandoned. It now comprises neighbourhoods and localities such as Frederiksstaden, the Nyboder neighbourhood, Nyhavn, Larsens Plads and Kongens Nytorv.
History
Expansion of the fortified city
As part of his aspirations to strengthen Copenhagen as a regional centre, Christian IV decided to expand the area of the fortified city northwards. As early as 1606, when his modernization of the fortifications began, he had purchased 200 hectares of land outside the Eastern City Gate. His intention was to redevelop this area into a new district referred to as Ny København (English: New Copenhagen) or Sankt Annæ By (Saint Ann's Town).[1] The plan was to change the course of Østervold, which at that time made a bend and ran along what is today Gothersgade and Kongens Nytorv. The new Østervold would be a direct extension of Nørrevold, connecting it to Sankt Annæ Skanse, thereby increasing the area of the fortified city with approximately 40%. However, the 1630s was a time of economic crisis and both Sankt Annæ Skanse and the new course of Østervold was delayed with no major work going on during that decade. After both Jutland and Scania had been occupied by enemy forces in the first half of the 1640s and the Kingdom's very existence had been threatened, work on the fortifications was resumed.
The new Østervold was constructed and a new project for the fortress at Sankt Annæ Skanse, with the layout of a bastioned pentagram, was completed in 1661.
References
- "Kongens Nytorv". Selskabet for Københavns Historie. Archived from the original on 2007-10-22. Retrieved 2009-08-25.