Neptunea antiqua
Neptunea antiqua, common name the red whelk, is a species of Northeast Atlantic sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Buccinidae, the true whelks.[1]
| Red whelk | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | N. antiqua |
| Binomial name | |
| Neptunea antiqua | |
Description
N. antiqua resembles Buccinum undatum (common whelk). It can grow to a length of 20 cm (7.9 in),[2] although most specimens only reach half that size.[3] It is the largest marine snail in parts of its range.[2]
Distribution
N. antiqua is found in the Northeast Atlantic along cold-temperate European coasts, ranging from the low water mark[4] to a depth of 1,200 m (3,900 ft).[3]
.jpg)
Feeding
N. antiqua is primarily a scavenger, although it has been recorded attacking and eating some living polychaete species.[4] Unlike several of its more predatory relatives, experiments have shown that even hungry N. antiqua are not attracted to living undamaged mussels.[4]
Food poisoning
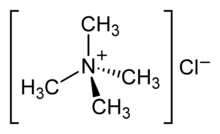
N. antiqua contains tetramethylammonium salts (most likely the chloride) in its tissues, and has been the source of non-lethal human poisoning. [5]
References
- Neptunea antiqua (Linnaeus, 1758). Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 17 April 2010.
- Naturstyrelsen: Rødkonk. Archived 11 September 2014 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- MarLIN: Red whelk - Neptunea antiqua. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- Pearce and Thorson (1967). The feeding and reproductive biology of the red whelk, Neptunea antiqua (L.) (Gastropoda, Prosobranchia). Ophelia 4(2): 277–314.
- U. Anthoni, L. Bohlin, C. Larsen, P. Nielsen, N. H. Nielsen, and C. Christophersen (1989). "The toxin tetramine from the "edible" whelk Neptunea antiqua." Toxicon 27 717–723.