Neoplanorbis tantillus
Neoplanorbis tantillus is a species of very small air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails. This species is endemic to the United States. In 2012, it has been declared extinct by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.[1]
| Neoplanorbis tantillus | |
|---|---|
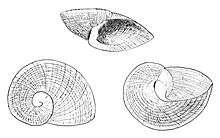 | |
| Three views of a shell of Neoplanorbis tantillus oriented as if it were a dextral shell. (All planorbids are in fact sinistral.) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | Neoplanorbinae |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | N. tantillus |
| Binomial name | |
| Neoplanorbis tantillus | |
The shells of this species appear to be dextral in coiling, but as is the case in all planorbids, the shell is actually sinistral. The shell is carried upside down with the aperture on the right, and this makes it appear to be dextral.
Original description
Species Neoplanorbis tantillus was originally described by Henry Augustus Pilsbry in 1906.[2]
Type locality is Coosa River near or in Wetumpka, Alabama.
Pilsbry's original text (the type description) reads as follows:
Neoplanorbis tantillus n. sp. PI. III, figs. 3, 4, 5.
Shell very narrowly perforate, slightly convex above, very convex below, with a strongly projecting rounded keel at the periphery; light brown; surface slightly shining, sculptured with very obliquely radial growth-lines and raised spiral stride, rather coarse for a shell of this size. Whorls 2, rapidly enlarging, the apex somewhat sunken; first whorl very convex, the second much less so, slowly descending in front. Aperture very oblique, shaped like a gothic-arched door, the upper and lower margins arcuate, the outer margin angular, the columellar margin dilated, straight and vertical, with a rather wide whitish callus within. Alt. .8, diam. 1.7 mm.
The specimens occurred at Wetumpka, Alabama with the preceding species. This is one of the smallest fresh-water mollusks yet found in America.
Note: "preceding species" in the description means Amphigyra alabamensis, because these two species were newly described in the same work.
References
- Cordeiro, J. & Perez, K. (2012). "Neoplanorbis tantillus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012: e. Retrieved 10 November 2017.{{cite iucn}}: error: malformed |page= identifier (help)
- Pilsbry H. A. (September 1906). "Two new American genera of Basommatophora". The Nautilus 20(5): 49–51.
