Naval Station San Miguel
Naval Station San Miguel is an installation of the Philippine Navy located in Barangay San Miguel, San Antonio, Zambales, The Philippines. The United States turned over the base to the Philippine government in 1992.
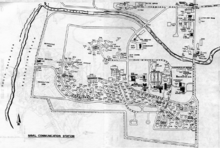
History

The U.S. Naval Communication Station, Philippines (NAVCOMSTAPHIL) had been established in the Philippines for a number of years. Construction at San Miguel began in early 1955. The preactivation detail moved to San Miguel from Sangley Point RP in July 1957 and the balance of the officers and men moved in increments. In January 1958 operations at Sangley Point were terminated and full scale operations at San Miguel commenced.
The base was named for the tiny fishing village of San Miguel which is adjacent to the southern end of the station. The base is located in a semicircular bowl of 1,737 acres (7.03 km2), surrounded by mountains on three sides, and the South China Sea on the fourth.
The primary purpose of the station was to provide communications to U.S Navy ships operating in the area of the Philippines.
During the Vietnam War, all communications from Vietnam to the Continental United States were routed first through here by an undersea cable from Nha Trang, then forwarded to Naval Link Station Mount Santa Rita, then to the Dau relay facility at Clark AFB, and finally to the HF transmitter site at the U.S. Naval Radio Station Tarlac also known as U.S. Naval Radio Transmitter Facility, Capas, Tarlac.
The base also housed a Marine barracks.
The United States turned over the base to the Philippine government in 1992. After its turnover, the Philippine Navy (PN), subsequently transferred its Naval Training Command from Fort San Felipe, Cavite to Naval Station San Miguel. It is now the home of the Philippine Navy's Naval Education and Training Command.
See also
- U.S. Naval Radio Facility Bagobantay
- US Naval Communication Facility, San Miguel, Philippines - "Welcome Aboard" Handbook 1958