Nature Reserve of Saint Bartholomew
Nature Reserve of Saint Bartholomew (Réserve Naturelle de Saint-Barthélemy) is a nature reserve of Saint Barthélemy (RNN 132), French West Indies, an overseas collectivity of France.
| Nature Reserve of Saint Bartholomew | |
|---|---|
| Réserve Naturelle de Saint-Barthélemy | |
IUCN category II (national park) | |
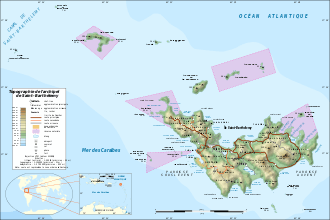 Areas within Nature Reserve of Saint Bartholomew are shaded purple. | |
| Location | Saint Barthélemy |
| Coordinates | 62°50′57″S 17°55′52″E |
| Area | 1,200 ha (3,000 acres) |
| Established | 1996 |
| Governing body | Grenat Association |
| Website | reservenaturellestbarth |

Background
Founded in 1996, it covers 1,200 hectares in five sectors: Gros Îlets and Pain de Sucre off Gustavia harbour; the waters surrounding the islets Fourchue, Frégate and Île Toc Vers; and part of Colombier bay. Protected marine areas of the reserve are demarcated on nautical charts of the region.[1] The management of the reserve rests with the Grenat Association.[2] It was established in 1996 with the objective of conserving coral reefs, sea grass beds and the marine life.[3] The reserve has coral formations in an area of 275 hectares (680 acres).
Fauna
45 coral species are recorded, apart from Ascidiacea, sea sponges and anemones. Sea urchins, starfish, shellfish, crustaceans, a few sea turtles and 165 species of fish are also reported.[3] An invasive species of fish found in this reserve is the lion fish, which is poisonous and has a dangerous bite.[4] The reserve is the habitat of 80 species of birds. The land area is small and its xerophytic vegetation is grazed by goats, causing loss of nestling ground for 15 terrestrial birds. Six species of water birds have also been recorded in the ponds of the island. The bird population witnesses a boost during the winter when a large number of Neotropical migrant birds flock the area. Within the reserve three bird areas have been identified by BirdLife International, which cover an area of 1,050 hectares (2,600 acres), apart from 0.4% of the land area of Saint Barthélemy. The key bird species recorded here are: brown booby (Sula leucogaster); laughing gull (Leucophaeus atricilla); royal tern (Thalasseus maximus); and common tern (Sterna hirundo).[2]
References
- ProStar 2004, p. 123.
- "St Barthelemy (to France)" (pdf). BirdLife International. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- Greenberg 2003, p. 47.
- "Battle against the lionfish". Natural Reserve of Saint Bartholomew.
Bibliography
- Greenberg, Harriet (1 April 2003). St. Martin and St. Barts Alive!. Hunter Publishing, Inc. ISBN 978-1-58843-356-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- ProStar (1 January 2004). ProStar Sailing Directions 2004 Caribbean. Volume 1 Enroute. ProStar Publications. ISBN 978-1-57785-567-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links

- Official website