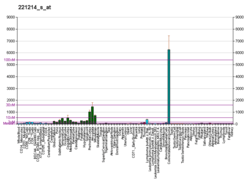
Nasal embryonic LHRH factor
Nasal embryonic luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NELF gene.[5][6][7]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000165802 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000006476 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, Gassenhuber J, Glassl S, Ansorge W, Böcher M, Blöcker H, Bauersachs S, Blum H, Lauber J, Düsterhöft A, Beyer A, Köhrer K, Strack N, Mewes HW, Ottenwälder B, Obermaier B, Tampe J, Heubner D, Wambutt R, Korn B, Klein M, Poustka A (Mar 2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Research. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- Kramer PR, Wray S (Jul 2000). "Novel gene expressed in nasal region influences outgrowth of olfactory axons and migration of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) neurons". Genes & Development. 14 (14): 1824–34. doi:10.1101/gad.14.14.1824. PMC 316793. PMID 10898796.
- "Entrez Gene: NELF nasal embryonic LHRH factor".
Further reading
- Miura K, Acierno JS, Seminara SB (2004). "Characterization of the human nasal embryonic LHRH factor gene, NELF, and a mutation screening among 65 patients with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH)". Journal of Human Genetics. 49 (5): 265–8. doi:10.1007/s10038-004-0137-4. PMID 15362570.
- Nousiainen M, Silljé HH, Sauer G, Nigg EA, Körner R (Apr 2006). "Phosphoproteome analysis of the human mitotic spindle". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 103 (14): 5391–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507066103. PMC 1459365. PMID 16565220.
- Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C, Patel AJ, Szabó G, Rual JF, Fisk CJ, Li N, Smolyar A, Hill DE, Barabási AL, Vidal M, Zoghbi HY (May 2006). "A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration". Cell. 125 (4): 801–14. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032. PMID 16713569.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.