Myoepithelioma of the head and neck
Myoepithelioma of the head and neck, also myoepithelioma, is a salivary gland tumour of the head and neck that is usually benign.[1]
| Myoepithelioma of the head and neck | |
|---|---|
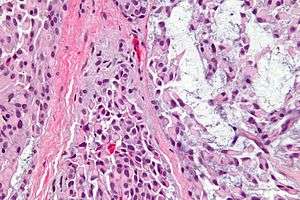 | |
| Micrograph of a myoepithelioma. H&E stain. | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
As the name suggests, it consists of myoepithelial cells. Classically, they are found in the parotid gland or palate.[1] A similar tumor type may be found in the tongue, referred to as ectomesenchymal chondromyxoid tumor.
Pathology
The myoepithelial cells may be spindled, plasmacytoid, eithelioid or clear. Tubules or epithelium are absent, or present in a small amount (<5%) by definition. Tumours with myoepithelial cells and a large amount of tubules are classified as pleomorphic adenomas (which must also contain the characteristic chondromyxoid stroma, which is normally absent in myoepithelioma).
Diagnosis
Myoepitheliomas are diagnosed from an examination of the tissue by a pathologist.
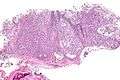 Low mag.
Low mag.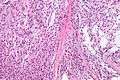 High mag.
High mag.
Treatment
Benign myoepithelioma are treated with simple excision. They are less prone to recurrence than pleomorphic adenoma.
References
- Barnes, L.; Appel, BN.; Perez, H.; El-Attar, AM. (Jan 1985). "Myoepithelioma of the head and neck: case report and review". J Surg Oncol. 28 (1): 21–8. doi:10.1002/jso.2930280107. PMID 2982059.
- Smith BC, Ellis GL, Meis-Kindblom JM, Williams SB (May 1995). "Ectomesenchymal chondromyxoid tumor of the anterior tongue. Nineteen cases of a new clinicopathologic entity". Am J Surg Pathol. 19 (5): 519–30. doi:10.1097/00000478-199505000-00003. PMID 7726361.