Mycobacillin
Mycobacillin is an antifungal cyclic peptide. It was first isolated in 1958 from the bacteria Bacillus subtilis.[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
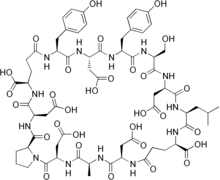
Cyclo(L-alanyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-prolyl-D-α-aspartyl-D-γ-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-L-α-aspartyl-L-tyrosyl-L-seryl-D-α-aspartyl-L-leucyl-D-γ-glutamyl-D-α-aspartyl) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C65H85N13O30 | |
| Molar mass | 1528.44 g/mol |
| Melting point | 235 to 240 °C (455 to 464 °F; 508 to 513 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Banerjee, A. B.; Bose, S. K. (1963). "Amino acid configuration of mycobacillin". Nature. 200 (4905): 471. Bibcode:1963Natur.200..471B. doi:10.1038/200471a0. PMID 14076732.
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 6234.
- Majumdar, S. K.; Bose, S. K. (1958). "Mycobacillin, a new antifungal antibiotic produced by Bacillus subtilis". Nature. 181 (4602): 134–5. doi:10.1038/181134a0. PMID 13493627.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.