Multiple models
In control theory, multiple models is an approach to improve efficiency of adaptive system or observer system. It uses large number of models, which are distributed in the region of uncertainty, and based on the responses of the plant and the models. One model is chosen at every instant, which is closest to the plant according to some metric. The method offers satisfactory performance when no restrictions are put on the number of available models. [1]
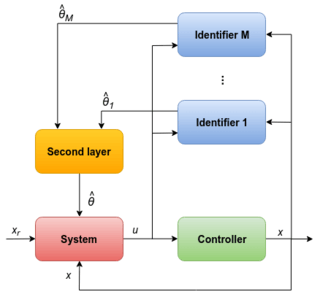
Adaptive Control with Multiple Models
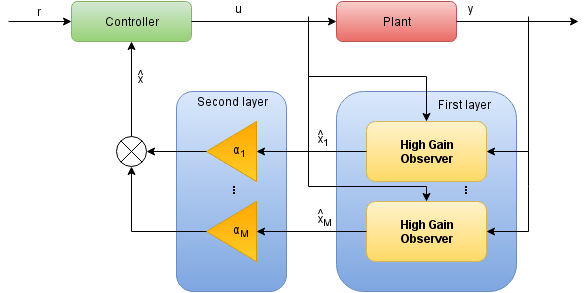
Multi Observer Schema
Approaches
There are two multiple model methods:
- “Switching” the control input to the plant is based on the fixed model chosen at that instant. It is discontinuous, fast, but coarse.
- “Switching and tuning”, an adaptive model is initialized from the location of the fixed model chosen, and the parameters of the best model determine the control to be used. It is continuous, slow, but accurate.
Applications
Multiple model method can be used for:
- controlling an unknown plant - parameter estimate and the identification errors can be used collectively to determine the control input to the overall system,
- applying multi observer - significantly improve transients and reduce observer overshoot.[2]
gollark: This should maybe work sometimes.
gollark: `entity.displayName == entity.name`
gollark: @Taikagreippi: um, I had a heuristic for it.
gollark: Can they?
gollark: But what if somebody accidentally plugs potatOS into an outlet?
See also
References
- Narendra, Kumpati S.; Han, Zhuo (August 2011). "Adaptive Control Using Collective Information Obtained from Multiple Models". International Federation of Automatic Control. 18 (1): 362–367. doi:10.3182/20110828-6-IT-1002.02237.
- Bernat, J.; Stepien, S. (2015), "Multi modelling as new estimation schema for High Gain Observers", International Journal of Control, 88 (6): 1209–1222, doi:10.1080/00207179.2014.1000380
General references
- Narendra, K.S.; Balakrishnan, J. (September 1994), "Improving Transient Response of Adaptive Control Systems Using Multiple Models and Switching", IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control: 1861–1866, doi:10.1109/9.317113
- Postoyan, R.; Hamid, M. H. A.; Daafouz, J. (December 2015), "A multi-observer approach for the state estimation of nonlinear systems", 2015 54th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control: 1793–1798, doi:10.1109/CDC.2015.7402470
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.