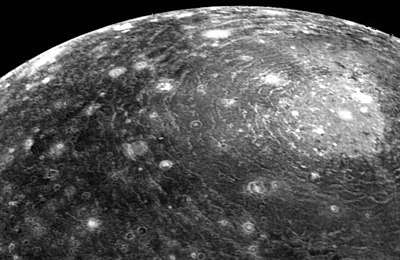
Multi-ringed basin
A multi-ringed basin (also a multi-ring impact basin) is not a simple bowl-shaped crater, or a peak ring crater, but one containing multiple concentric topographic rings;[1] a multi-ringed basin could be described as a massive impact crater, surrounded by circular chains of mountains.[2] As such, a multi-ring basin slightly resembles a bull's-eye, may have an area of many thousands of square kilometres.[3]
An impact crater of diameter bigger than about 180 miles (290 km) is referred to as a basin.[4]
.png)
The structure of multi-ring basins
In adjacent rings, the ratio of the diameters approximates √2:1 ≈ 1.41 to 1.[5][6]
Formation
To start, a peak ring crater has
- one peak-ring, i.e., a crater rim, which is generally circular, and
- a mountainous region which surrounds the basin center.
A multi-ringed basin has an important difference, which is multiple peak-rings.
In extremely large collisions, following the impact the rebound of the surface can obliterate any trace of the initial impact point. Usually a peak ring crater has a high structure with a terrace, and has slump structures inside of it. There are new theories about the lunar mare called Mare Orientale on Earth's Moon, as to how it formed.[7]
Multi-ring basins are some of the largest, oldest, rarest and least understood of impact craters. There are various theories to explain the formation of multi-ringed basis, however there is currently, there is no consensus.[8][9]
Examples
- In Mexico Chicxulub crater has a sufficient area to have been a multi-ringed basin,[10]
- On the largest moon of Jupiter, Ganymede, Anubis Crater is a multi-ringed basin,
- On the moon of Saturn, Dione, Evander is a multi-ringed basin,
- On Mercury, Caloris Basin, surrounded by Caloris Montes is a multi-ringed basin,
- The Earth's Moon, Mare Orientale is a multi-ringed basin, created by an impactor perhaps 285 miles in diameter, near as wide as the state of New York, traveling at 9 miles per second, or about 32,400 miles per hour,[11]
- On Jupiter's moon Callisto, Valhalla is a multi-ringed basin.
See also
- Central-peak crater
- Complex crater – large impact crater morphology with uplifted centres
- Impact crater – Circular depression on a solid astronomical body formed by a hypervelocity impact of a smaller object
- Impact event – Collision of two astronomical objects with measurable effects
- Impact structure
- Peak ring (crater) – A roughly circular ring or plateau, possibly discontinuous, surrounds the impact crater's center
- Pedestal crater
- Expanded crater
- Traces of Catastrophe book from Lunar and Planetary Institute - comprehensive reference on impact crater science
References
- Head, J. W. (January 2010). "Transition from complex craters to multi-ringed basins on terrestrial planetary bodies: Scale-dependent role of the expanding melt cavity and progressive interaction with the displaced zone" (PDF). Geophysical Research Letters. 37 (2): L02203. Bibcode:2010GeoRL..37.2203H. doi:10.1029/2009GL041790.
- "Lunar Landforms Teacher Page". Hawai'i Space Grant Consortium, Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology, University of Hawai'i. 1998. Retrieved 18 January 2019.
- "Multiringed basin". Encyclopedia Britannica. February 1, 2018. Retrieved January 20, 2019.
- Parrish, Alton (October 29, 2016). "How Multi-Ring Craters Form Revealed by New Research". Ideas, Inventions And Innovations. Retrieved January 20, 2019.
- "Multi-Ring Basin". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved January 20, 2019.
- Martellato, Elena (January 31, 2011). The importance of being a crater: A tool in planetary surface analysis and datation (PDF) (PhD Thesis). Università degli Studi di Padova. Retrieved January 20, 2019.
- Stacey, Kevin (October 27, 2016). "Research helps explain formation of ringed crater on the Moon". News from Brown. Retrieved 20 January 2019.
- Potter, Ross W.K. (November 2015). "Investigating the onset of multi-ring impact basin formation" (PDF). Icarus. 261: 91–99. Bibcode:2015Icar..261...91P. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2015.08.009.
- Stuart Ross Taylor (1982). "Meteorite impacts, craters and multi-ring basins" (PDF). Planetary Science: A Lunar Perspective. Lunar and Planetary Institute. Retrieved 19 January 2019.
- McKinnon, W. B.; Alexopoulos, J. S. "Some implications of large impact craters and basins on Venus for terrestrial ringed craters and planetary evolution". KT Event and Other Catastrophes. hdl:2060/19940023803.
- Chu, Jennifer (October 27, 2016). "Retracing the origins of a massive, multi-ring crater". MIT News. Retrieved 20 January 2019.
External links and references
- Transition from complex craters to multi‐ringed basins on terrestrial planetary bodies: Scale‐dependent role of the expanding melt cavity and progressive interaction with the displaced zone
- Retracing the origins of a massive, multi-ring crater