Mogroside
A mogroside is a glycoside of cucurbitane derivatives found in certain plants, such as the fruit of the gourd vine, luo han guo (Siraitia grosvenorii).[1][2] Mogrosides are extracted from S. grosvenorii and used in the manufacture of sugar substitutes.[1][2]
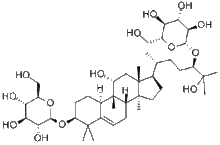
Mogrosides
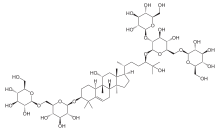
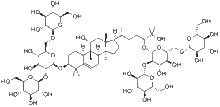
- Mogrol
- Mogroside II A1
- Mogroside II B
- 7-Oxomogroside II E
- 11-Oxomogroside A1
- Mogroside III A2
- 11-Deoxymogroside III
- 11-Oxomogroside IV A
- Mogroside V
- 7-Oxomogroside V
- 11-Oxo-mogroside V
- Mogroside VI
Biosynthesis
One analysis of 200 candidate genes of Siraitia grosvenorii revealed five enzyme families involved in the synthesis of mogroside V: squalene epoxidases, triterpenoid synthases, epoxide hydrolases, cytochrome P450s, and UDP-glucosyltransferases.[1] The metabolic pathway for mogroside biosynthesis involves an initial stage of fruit development when squalene is metabolized to di-glucosylated, tetra-hydroxycucurbitadienols, then during fruit maturation, branched glucosyl groups are added and catalyzed, leading to the sweet M4, M5, and M6 mogrosides.[1]
Uses
Some mogrosides are used in traditional Chinese medicine[2] and some are extracted for manufacturing as sweeteners.[1] Mogroside V extract from S. grosvenorii fruit is 250 times sweeter than sucrose.[1]
References
- Itkin, M.; Davidovich-Rikanati, R.; Cohen, S.; Portnoy, V.; Doron-Faigenboim, A.; Oren, E.; Freilich, S.; Tzuri, G.; Baranes, N.; Shen, S.; Petreikov, M.; Sertchook, R.; Ben-Dor, S.; Gottlieb, H.; Hernandez, A.; Nelson, D. R.; Paris, H. S.; Tadmor, Y.; Burger, Y.; Lewinsohn, E.; Katzir, N.; Schaffer, A. (2016). "The biosynthetic pathway of the nonsugar, high-intensity sweetener mogroside V from Siraitia grosvenorii". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (47): E7619–E7628. doi:10.1073/pnas.1604828113. PMC 5127336. PMID 27821754.
- Subhuti Dharmananda (January 2004), "Luo han guo - Sweet fruit used as sugar substitute and medicinal herb". Institute for Traditional Medicine, Portland, Oregon.
External links
