Mogno State Forest
The Mogno State Forest (Portuguese: Floresta estadual do Mogno) is a state forest in the state of Acre, Brazil.
| Mogno State Forest | |
|---|---|
| Floresta estadual do Mogno | |
 | |
| Nearest city | Tarauacá |
| Coordinates | 7°46′58″S 71°46′41″W |
| Area | 143,897 hectares (355,580 acres) |
| Designation | State forest |
| Administrator | Instituto de Meio Ambiente do Acre |
Location
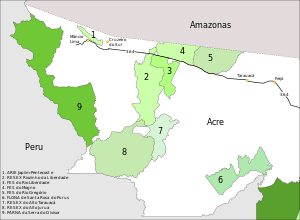
4. Mogno State Forest
The Mogno State Forest is in the municipality of Tarauacá in the state of Acre. It has an area of 143,897 hectares (355,580 acres).[1] It is bounded to the north by the border with the state of Amazonas, and adjoins the Rio Gregório Extractive Reserve in Amazonas. Its eastern boundary is defined by the Gregório River, which separates it from the Rio Gregório State Forest. The BR-364 highway forms the southern boundary. The Rio Liberdade State Forest and Riozinho da Liberdade Extractive Reserve adjoin it to the south and west, mainly lying to the south of the BR-364. To the west the Riozinho da Liberdade defines its boundary.[1]
History
The forest was created by decree of the governor of Acre on 9 March 2004. It was recognised by the Instituto Nacional de Colonização e Reforma Agrária (National Institute for Colonization and Agrarian Reform – INCRA) as an agro-extractive project for 210 families on 28 April 2005.[1] On 13 December 2010 INCRA changed the number of families to 177.[1] The consultative council for the Rio Gregório State Forest complex was created by decree on 19 September 2008. This covers the Rio Gregório, Mogno and Rio Liberdade state forests, all of which had been created on the same date.[2] The governor installed the council members in April 2012.[3]
People and economy
As of April 2012 there were 422 families in the Rio Gregório Forest Complex, which covered 480,000 hectares (1,200,000 acres) in total. The state's Department of Industry, Trade and Sustainable Services (SEDENS) had a number of plans for the complex. These included providing two new trucks to support the communities, making football fields in each community, providing coordinators to arrange meetings, resuming production of tree seedlings and providing assistance with family farming, small livestock and fish farming. Each family would get a concession of 100 hectares (250 acres) of which 20% could be cleared and the remainder used in a sustainable way. Wood processing factories were to be built in Cruzeiro do Sul and Tarauacá.[3]
Notes
Sources
- FES do Mogno (in Portuguese), ISA:Instituto Socoambiental, retrieved 2016-07-01
- "Governo instala Conselho no Complexo Florestal do Rio Gregório", A Gazeta do Acre (in Portuguese), 30 April 2012, retrieved 2016-07-01
- MOS Complexo de Florestas Estaduais do Rio Gregório (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-07-01