Micromyrtus grandis
Micromyrtus grandis, the Severn River heath-myrtle, is a shrub in the myrtle family. It is found exclusively in the Severn River Nature Preserve and a property next to it, located around 60 km north-west of Glen Innes (Australia). It grows up to 1–4 metres tall, making it the largest plant in the genus Micromyrtus. The Severn River heath-myrtle is characterized by its fruit, which is 5-ribbed, and its broader leaves when compared to other nearby flora.
| Micromyrtus grandis | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Myrtaceae |
| Genus: | Micromyrtus |
| Species: | M. grandis |
| Binomial name | |
| Micromyrtus grandis J.T.Hunter | |
Taxonomy and naming
John T. Hunter described Micromyrtus grandis in 1996, after coming across a colony of Micromyrtus on a porphyritic ridge that did not correspond to any known species. He gave it the species name grandis as it was the largest species in the genus.[1]
Description
Micromyrtus grandis grows as a shrub with an erect habit, reaching 1–4 metres tall.[2] The orange bark is stringy and shed in ribbons, which frequently curl.[3] The tiny leaves are 0.5 to 4 mm long by 0.5 to 1.5 mm wide. When held up to the light, their oil dots can be clearly seen in the leaf blade. The minuscule flowers appear over winter and spring (July to September).[2]
Distribution and habitat
Micromyrtus grandis is found along one long ridge at an altitude of 600 to 750 m in the Severn River Nature Preserve and adjoining private farmland.[1] It grows in exposed locations in heath and open woodland, associated with such species as narrow-leaved ironbark (Eucalyptus crebra), stringybark she-oak (Allocasuarina inophloia), ''Acacia'' sp. aff. ''pubifolia'', Johnson's grasstree (Xanthorrhoea johnsonii), and heath species Leptospermum novae-angliae, Micromyrtus sessilis and Leucopogon neo-anglicus.[2]
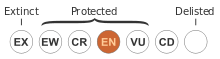
It is gazetted as endangered by both New South Wales and Federal governments.[2]
Cultivation
Micromyrtus grandis has been cultivated at the Australian National Botanic Gardens in Canberra since 1998, proving hardy and easy to grow, and can be propagated by seed or cutting.[3]
References
- Hunter, John T.; Quinn, Francis C.; Bruhl, Jeremy J. (1996). "Micromyrtus grandis (Myrtaceae), a new species from New South Wales". Telopea. 7 (1): 77–81.
- "Severn River Heath-myrtle". New South Wales Office of Environment and Heritage. 26 August 2014. Retrieved 2 November 2015.
- Jalaluddin, Susan (2012). "Micromyrtus grandis". Information about Australia's Flora: Growing Native Plants. Australian National Botanic Gardens and Centre for Australian National Biodiversity Research. Retrieved 4 November 2015.