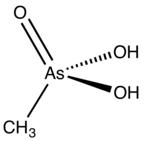
Methylarsonic acid
Methylarsonic acid is an organoarsenic compound with the formula CH3AsO3H2. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid. Salts of this compound, e.g. disodium methyl arsonate, have been widely used in as a herbicides and fungicides in growing cotton and rice.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
methanearsonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 4-04-00-03682 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.278 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1557 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH5AsO3 | |
| Molar mass | 139.970 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 160.5 °C (320.9 °F; 433.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Reactions
Near physiological pH, methanearsonic acid converts to its conjugate bases, the methylarsonates. These include CH3AsO3H− and CH
3AsO2−
3.
Synthesis and biosynthesis
Reaction of arsenous acid with methyl iodide gives methylarsonic acid. This historically significant conversion is called the Meyer reaction:[2]
- As(OH)3 + CH3I + NaOH → CH3AsO(OH)2 + NaI + H2O
The then novel aspect of the reaction was that alkylation occurs at As, leading to oxidation of As from III to V.
The biomethylation of arsenic compounds is thought to start with the formation of methanearsonates. Thus, trivalent arsenic compounds are methylated to give methanearsonate. S-adenosylmethionine is the methyl donor. The methanearsonates are the precursors to cacodylates, again by the cycle of reduction (to methylarsonous acid) followed by a second methylation.[3]
Safety
Like all arsenic compounds, it is highly toxic.[3]
References
- Grund, S. C.; Hanusch, K.; Wolf, H. U. "Arsenic and Arsenic Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_113.pub2.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- G. Meyer (1883). "Ueber einige anomale Reaktionen". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 13: 1439–1443. doi:10.1002/cber.188301601316.
- Styblo, M.; Del Razo, L. M.; Vega, L.; Germolec, D. R.; LeCluyse, E. L.; Hamilton, G. A.; Reed, W.; Wang, C.; Cullen, W. R.; Thomas, D. J. (2000). "Comparative toxicity of trivalent and pentavalent inorganic and methylated arsenicals in rat and human cells". Archives of Toxicology. 74: 289–299. doi:10.1007/s002040000134.