Methyl lactate
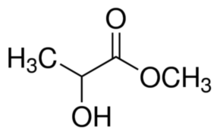
Methyl lactate, also known as lactic acid methyl ester, is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH(OH)CO2CH3. It is the methyl ester of lactic acid. A colorless liquid, it is the simplest chiral ester. Being naturally derived, it is readily available as a single enantiomer.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methyl 2-hydroxypropanoate | |
| Other names
2-Hydroxy- Methyl Ester Propanoic Acid; 2-Hydroxypropanoic Acid, Methyl Ester; Lactic Acid, Methyl Ester | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.119 |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 104.105 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colourless clear liquid |
| Density | 1.093 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −66 °C (−87 °F; 207 K) |
| Boiling point | 144 to 145 °C (291 to 293 °F; 417 to 418 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Solubility in ethanol and most alcohols |
Miscible |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant (Xi) |
| Safety data sheet | MSDS |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
|
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 49 °C (120 °F; 322 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Lactic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Uses
It is a solvent for nitrocellulose, cellulase acetate, cellulase acetobutyrote and cellulase acetaprapionate. It is used in the manufacture of lacquers and dopes where it contributes high tolerance for diluents, good flaw and blush resistance.[1]
The synthesis of 1,2-propanediol from methyl lactate has been commercialized using a MACHO catalyst.[2]
gollark: It's a 2G floret, not much room for fancy lineageing.
gollark: Hold on while I append ARBITRARYPREFIX!
gollark: Also, are you suggesting that if I append "ARBITRARYPREFIX" to a few dragons I'll suddenly get twice the offers?
gollark: Are you sure it's not because florets?
gollark: What, really?
See also
- Ethyl lactate, a more commonly used ester of lactic acid
References
- "Industrial Solvents Handbook" by Ernest W. Flick. 5th Edition. William Andrew Inc., 1998. ISBN 0-8155-1413-1, ISBN 978-0-8155-1413-8
- Dub, Pavel A.; Gordon, John C. (2018). "The role of the metal-bound N–H functionality in Noyori-type molecular catalysts". Nature Reviews Chemistry. 2 (12): 396–408. doi:10.1038/s41570-018-0049-z. S2CID 106394152.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
