Meredith graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Meredith graph is a 4-regular undirected graph with 70 vertices and 140 edges discovered by Guy H. J. Meredith in 1973.[1]
| Meredith graph | |
|---|---|
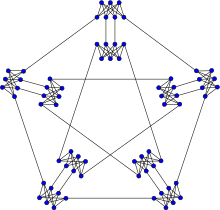 The Meredith graph | |
| Named after | G. H. Meredith |
| Vertices | 70 |
| Edges | 140 |
| Radius | 7 |
| Diameter | 8 |
| Girth | 4 |
| Automorphisms | 38698352640 |
| Chromatic number | 3 |
| Chromatic index | 5 |
| Book thickness | 3 |
| Queue number | 2 |
| Properties | Eulerian |
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
The Meredith graph is 4-vertex-connected and 4-edge-connected, has chromatic number 3, chromatic index 5, radius 7, diameter 8, girth 4 and is non-hamiltonian.[2] It has book thickness 3 and queue number 2.[3]
Published in 1973, it provides a counterexample to the Crispin Nash-Williams conjecture that every 4-regular 4-vertex-connected graph is Hamiltonian.[4][5] However, W. T. Tutte showed that all 4-connected planar graphs are hamiltonian.[6]
The characteristic polynomial of the Meredith graph is .
Gallery
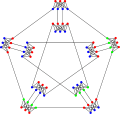 The chromatic number of the Meredith graph is 3.
The chromatic number of the Meredith graph is 3.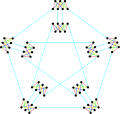 The chromatic index of the Meredith graph is 5.
The chromatic index of the Meredith graph is 5.
gollark: What?
gollark: You can do that, it'll probably typeerror.
gollark: Yes.
gollark: OOP isn't *that* apioformic.
gollark: That is why they are "public".
References
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Meredith graph". MathWorld.
- Bondy, J. A. and Murty, U. S. R. "Graph Theory". Springer, p. 470, 2007.
- Jessica Wolz, Engineering Linear Layouts with SAT. Master Thesis, University of Tübingen, 2018
- Meredith, G. H. J. "Regular 4-Valent 4-Connected Nonhamiltonian Non-4-Edge-Colorable Graphs." J. Combin. Th. B 14, 55-60, 1973.
- Bondy, J. A. and Murty, U. S. R. "Graph Theory with Applications". New York: North Holland, p. 239, 1976.
- Tutte, W.T., ed., Recent Progress in Combinatorics. Academic Press, New York, 1969.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.