Medronic acid
Medronic acid (conjugate base, medronate), also known as methylene diphosphonate, is the smallest bisphosphonate. Its complex with radioactive technetium, 99mTc medronic acid, is used in nuclear medicine to detect bone abnormalities, including metastases.
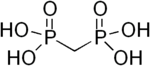 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
methanediylbis(phosphonic acid) | |
| Other names
methanediphosphonic acid; methylenebis(phosphonic acid); methylene diphosphonate; medronate; phosphonomethylphosphonic acid; MDP | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.229 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH6O6P2 | |
| Molar mass | 176.001 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 199 to 200 °C (390 to 392 °F; 472 to 473 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
45-50 mg/kg (i.v., mice, rabbits)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Budavari, Susan, ed. (1996), The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (12th ed.), Merck, ISBN 0911910123
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.