McNally (crater)
McNally is a crater that is located to the north-northwest of the much larger crater Fersman, on the far side of Moon. This is a worn crater with a rounded rim edge that is marked by many tiny impacts. Smaller, cup-shaped impacts cut through the rim along the southeastern and northern edges. There is a small craterlet along the base of the southeastern inner wall. The interior floor is otherwise relatively featureless. The crater is named after the Jesuit astronomer and Catholic priest Paul A. McNally.
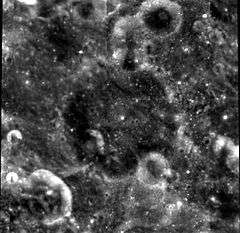 Clementine mosaic | |
| Coordinates | 22.6°N 127.2°W |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 47 km |
| Depth | Unknown |
| Colongitude | 128° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Paul A. McNally |

Oblique Lunar Orbiter 5 image. Spots in lower right are blemishes on original.
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to McNally.
| McNally | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 22.3° N | 129.0° W | 19 km |
| Y | 24.2° N | 127.5° W | 22 km |
gollark: Oops. No idea how that happened.
gollark: However, it is known that Superconducting digital logic circuits use single flux quanta (SFQ), also known as magnetic flux quanta, to encode, process, and transport data. SFQ circuits are made up of active Josephson junctions and passive elements such as inductors, resistors, transformers, and transmission lines. Whereas voltages and capacitors are important in semiconductor logic circuits such as CMOS, currents and inductors are most important in SFQ logic circuits. Power can be supplied by either direct current or alternating current, depending on the SFQ logic family.
gollark: Oh, I forgot those.
gollark: Oh, backslashes are bad.
gollark: Well, shell has accursuous quoting rules.
References
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. Retrieved 2007-08-05.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.