Local tangent plane coordinates
Local tangent plane coordinates (LTP), sometimes named local vertical, local horizontal coordinates (LVLH), are a geographical coordinate system based on the local vertical direction and the Earth's axis of rotation. It consists of three coordinates: one represents the position along the northern axis, one along the local eastern axis, and one represents the vertical position. Two right-handed variants exist: east, north, up (ENU) coordinates and north, east, down (NED) coordinates. They serve for representing state vectors that are commonly used in aviation and marine cybernetics.
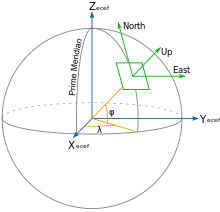
Axes
These frames are location dependent. For movements around the globe, like air or sea navigation, the frames are defined as tangent to the lines of geographical coordinates:
Local east, north, up (ENU) coordinates
In many targeting and tracking applications the local East, North, Up (ENU) Cartesian coordinate system is far more intuitive and practical than ECEF or Geodetic coordinates. The local ENU coordinates are formed from a plane tangent to the Earth's surface fixed to a specific location and hence it is sometimes known as a "Local Tangent" or "local geodetic" plane. By convention the east axis is labeled , the north and the up .
Local north, east, down (NED) coordinates
In an airplane, most objects of interest are below the aircraft, so it is sensible to define down as a positive number. The North, East, Down (NED) coordinates allow this as an alternative to the ENU. By convention, the north axis is labeled , the east and the down . To avoid confusion between and , etc. in this article we will restrict the local coordinate frame to ENU.
The origin of this coordinate system is usually chosen to be a point on the surface of the geoid below the aircraft's center of gravity. However, care must be taken since, if the aircraft is accelerating (turning or accelerating linearly), then the NED coordinates are no longer inertial coordinates.[1]
NED coordinates are similar to ECEF in that they're Cartesian, however they can be more convenient due to the relatively small numbers involved, and also because of the intuitive axes. NED and ECEF coordinates can be related with the following formula:[2]
where is a 3D position in a NED system, is the corresponding ECEF position, is the reference ECEF position (where the local tangent plane originates), and is a rotation matrix whose columns are the north, east, and down axes. may be defined conveniently from the latitude and longitude corresponding to :
See also
- Axes conventions
- Geodetic system
References
- Cai, Guowei; Chen, Ben M.; Lee, Tong Heng (2011). Unmanned Rotorcraft Systems. Springer. pp. 27. ISBN 978-0-85729-634-4.
- Cai, Guowei; Chen, Ben M.; Lee, Tong Heng (2011). Unmanned Rotorcraft Systems. Springer. pp. 32. ISBN 978-0-85729-634-4.