Litke Deep
Litke Deep (Russian: Жолоб Ли́тке) is[1][2] an oceanic trench in the Arctic Ocean.
Geography
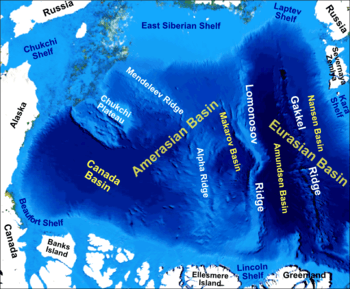
The Litke Deep is located in the southwestern part of the Eurasian Basin,[3] which stretches from northeastern part of Greenland past the Svalbard archipelago, Franz Josef Land and Severnaya Zemlya to the Taymyr Peninsula. It is situated south of the underwater ridge Gakkel Ridge roughly 350 kilometers[4] northeast of Svalbard and roughly 220 km north of the island of Nordaustlandet. The deepest part is at 5,449 metres[2] (17,881 feet)[3][5][6] under sea level. The average depth in the Arctic Ocean is about 1,000 metres[5] and more than 60 % is less than 200 metres deep.[1]
While the Litke Deep has been claimed to be the deepest point in the Arctic, this title in fact belongs to the Molloy Deep in the Fram Strait in the Greenland Sea.[7][8][9][10][11]
History
The Litke Deep was located in 1955[2] by the Russian icebreaker Fyodor Litke[12] expedition. It is named after Russian explorer Fyodor Petrovich Litke.[4]
See also
References
- "The Great Challenge of the Artic" (PDF). Ministry for Europe and Foreign Affairs gouv.fr, p 7. Retrieved 6 June 2017.
- "Hydrography of the Arctic Ocean with Special Reference to the Beaufort Sea" (PDF). Kou Kusunoki, Hokkaido University, p 4. Retrieved 6 June 2017.
- "What Is An Oceanic Trench". Worldatlas.com. Retrieved 6 June 2017.
- "chapter The Arctic Ocean". Sharon Chester, The Arctic Guide: Wildlife of the Far North, p 19. Retrieved 6 June 2017.
- "Introducing the Arctic Ocean" (PDF). Alaskawild.org, p 2. Retrieved 6 June 2017.
- International Council of Scientific Unions, International Geophysical Committee (1969). Annals of the International Geophysical Year, Volumes 46-48 p.99 Oxford: Pergamon Press
- Klenke, Martin; Schenke, Hans Werner (2002-07-01). "A new bathymetric model for the central Fram Strait". Marine Geophysical Researches. 23: 367–378. doi:10.1023/A:1025764206736.
- Bourke, Robert; Tunnicliffe, Mark; Newton, John; Paquette, Robert; Manley, Tom (1987-06-30). "Eddy near the Molloy Deep revisited". Journal of Geophysical Research. 92: 6773–6776. doi:10.1029/JC092iC07p06773.
- Thiede, Jörn; Pfirman, Stephanie; Schenke, Hans Werner; Reil, Wolfgang (1990-08-01). "Bathymetry of Molloy Deep: Fram Strait between Svalbard and Greenland". Mar. geophys. Res. 12: 197–214. doi:10.1007/BF02266713.
- Freire, Francis; Gyllencreutz, Richard; Jafri, Rooh; Jakobsson, Martin (2014-03-31). "Acoustic evidence of a submarine slide in the deepest part of the Arctic, the Molloy Hole". Geo-Marine Letters. 34. doi:10.1007/s00367-014-0371-5.
- "Five Deeps Expedition is complete after historic dive to the bottom of the Arctic Ocean" (PDF).
- "Voyage of the Fedor Litke". Cambridge University, Polar Record, vol 8, nr 52, p 27. Retrieved 6 June 2017.