Lighthouse of Ponta de Sagres
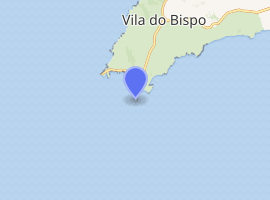
The Lighthouse of Ponta de Sagres (Portuguese: Estação Rádio-Goniométrica/Farolim de Sagres/Farol da Ponta de Sagres), is beacon/lighthouse located along the coastal peninsula of Sagres Point in the civil parish of Sagres, in the Portuguese municipality of the Vila do Bispo.
 The lighthouse at the point in Sagres | |
 Portugal | |
| |
| Location | Cape St. Vincent Sagres Vila do Bispo Portugal |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 36°59′40.4″N 8°56′57.7″W |
| Year first constructed | 1894 (first) 1923 (second) |
| Year first lit | 1960 (current) |
| Automated | 1979 |
| Foundation | concrete |
| Construction | concrete tower |
| Tower shape | square tower with balcony and lantern |
| Markings / pattern | unpainted tower, white lantern, red lantern roof |
| Tower height | 13 metres (43 ft) |
| Focal height | 53 metres (174 ft) |
| Intensity | 500 W |
| Range | 20 kilometres (12 mi) |
| Characteristic | Iso R 2s. |
| Admiralty number | D-2170 |
| NGA number | 3620 |
| ARLHS number | POR-043 |
| Portugal number | PT-440[1] |
| Heritage | Included in protected site |
History

As part of the 5th centenary commemorations marking the birth of Henry the Navigator, in 1894 the lighthouse was inaugurated.[2] The third navigational advisory, dated 3 March 1894, indicated that he light was a fixed red beacon, with a 5 miles (8.0 km), using a petroleum lamp.
On 28 November 1906, the 5th order diopter lamp was substituted by an optical device of greater range. This lantern was lit on 23 June 1923, following the construction of a new building with the installation of a 4th order catadioptric optical lamp, that was originally installed in the lighthouse of Ponta da Piedade.[2]
Between 1947-1949, the lighthouse was transferred to the Ministry of the Navy.[2]
The illumination source was changed to an electric incandescent lamp following the installation of power generators.[2]
In 1958, it was decided to demolish the building, due to its historic inadequacy, and a new structure was constructed 20 metres (66 ft) from the old building.[2] Budgeted at 146.890$00 escudos (733.00 euros), the new lighthouse was inaugurated on 1 April 1960.
The lighthouse was automatized in 1979.[2]
In August 1983, the lighthouse began to be controlled from a distance, from the Cape St. Vincent Lighthouse, and integrated into the special protection zone of the fortress of Sagres.[2]
Architecture
The lighthouse tower is 13 metres (43 ft), the light is located at about 53 metres (174 ft) altitude and has a range of 20 kilometres (12 mi).[2] The lamp is characterized by a luminous red beacon that flashes at a two-second interval.[2] The rotation of the optical beacon is produced from clock mechanism.
The building consists of a rectangular tower of white masonry, with a single-story annex for the residence of the lighthouse-keeper and storage of material, measuring 5.5 metres (18 ft) to the cornices.[2]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sagres Lighthouse. |
- Notes
- Ponta de Sagres The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved March 19, 2016
- Viegas, Patrícia; Ferreira, Teresa (2012), SIPA (ed.), Estação Rádio-Goniométrica/Farolim de Sagres/Farol da Ponta de Sagres (IPA.00017069/PT050815040015) (in Portuguese), Lisbon, Portugal: SIPA – Sistema de Informação para o Património Arquitectónico, archived from the original on 10 November 2013, retrieved 6 November 2013
- Sources
- Relatório da Actividade do Ministério no Triénio de 1947 a 1949, Lisbon, Portugal: Ministério das Obras Públicas, 1950
- "Ponta de Sagres", NGA List of Lights, NGA: National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, 26 September 2009
- Informações, Associação Náutica da Marina do Parque das Nações, 20 December 2002
- Novo Sistema de Radionavegação de Base Terrestre, Marinha Portuguesa, 21 October 2005
- "Farol de Sagres", Revista da Armada (in Portuguese), Marinha de Guerra Portuguesa, May 2006